Laser Reveals Whether You've Been Eating Your Veggies
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
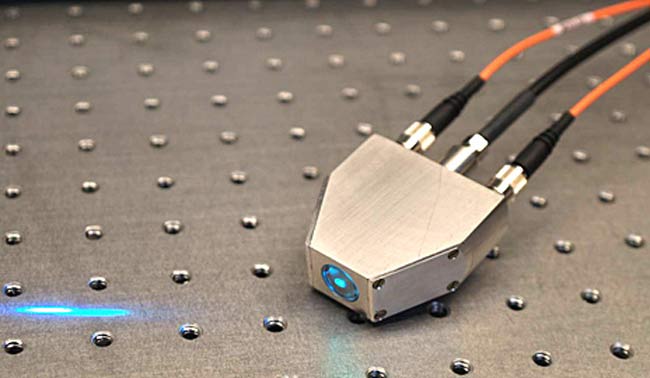
Lying about eating your fruits and vegetables won't save you when facing the unflinching gaze of a blue laser beam. That's because shining a blue laser light on human skin can detect biomarkers that tell whether fruits and vegetables figure into a person's diet, researchers say.
The simple method works by revealing carotenoid pigments such as beta-carotene in carrots and lycopene in tomatoes. A modern version of a decades-old technology called resonance Raman spectroscopy (RRS) can detect the energy changes in molecules after being energized by the laser light — a painless process that returns results in about a minute.
"It really derived from an observation that people have known about for decades," said Susan Mayne, head of chronic disease epidemiology at Yale University, "and that is that when people have high-vegetable diets they develop a yellow skin coloration that is particularly noticeable in the palm of the hand because of the accumulation of carotenoids in the skin."
"And we thought, 'Can we use that as a new approach to measure carotenoids in the body noninvasively?'"
The flash of insight came out of a chance meeting between Mayne and Werner Gellermann, a laser physicist at the University of Utah, during a long airline flight. The physicist explained how he was using lasers to detect carotenoid levels in the human eye's retina, because researchers believe high levels in the retina protect against macular degeneration.
The possibility of detecting carotenoids in such a simple manner excited Mayne. She knew that nutritionists currently measure biomarkers by taking blood, urine or skin samples from unhappy patients — a costly and painful process. [No More 'Ouch': New Injector Painlessly Delivers Drugs]
Mayne and her physicist seatmate worked out a grant proposal by the time their plane had landed. Testing of the first prototype device showed the laser method compared well with the current blood-and-skin testing that represents today's gold standard (as well as a 2010 study in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition).
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The new Raman and laser technique still needs some tweaking. Researchers need to figure out how long carotenoids last in the skin, so that they can tell whether a measurement reflects days or weeks worth of fruit and vegetable consumption. They also need to study how well the device can detect changes in carotenoid levels that reflect changes in a person's diet of fruits and vegetables.
But success could mean many happier nutritionists and physicians — not to mention parents and kids. The device has already helped scan 60 preschool kids without any fuss in the span of one afternoon's naptime.
This story was provided by InnovationNewsDaily, a sister site to LiveScience. You can follow InnovationNewsDaily on Twitter @News_Innovation, or on Facebook.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus