Ancient Mariners: Did Neanderthals Sail to Mediterranean?
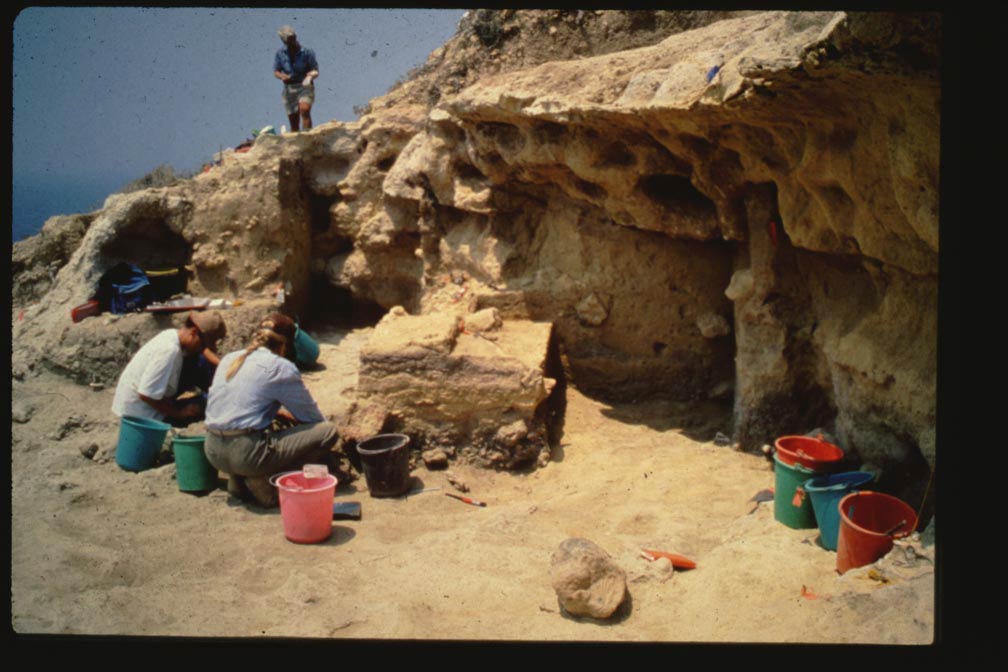

Neanderthals and other extinct human lineages might have been ancient mariners, venturing to the Mediterranean islands thousands of years earlier than previously thought.
This prehistoric seafaring could shed light on the mental capabilities of these lost relatives of modern humans, researchers say.
Scientists had thought the Mediterranean islands were first settled about 9,000 years ago by Neolithic or New Stone Age farmers and shepherds.
"On a lot of Mediterranean islands, you have these amazing remains from classical antiquity to study, so for many years people didn't even look for older sites," said archaeologist Alan Simmons at the University of Nevada at Las Vegas.
However, in the last 20 years or so, some evidence has surfaced for a human presence on these islands dating back immediately before the Neolithic. [Image Gallery: Our Closest Human Ancestor]
"There's still a lot to find in archaeology — you have to keep pushing the envelope in terms of conventional wisdom," Simmons said.
Neanderthal sailors?
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
For instance, obsidian from the Aegean island of Melos was uncovered at the mainland Greek coastal site of Franchthi cave in layers that were about 11,000 years old, while excavations on the southern coast of Cyprus revealed stone artifacts about 12,000 years old.
"We found evidence that human hunters may have helped drive pygmy hippos to extinction on Cyprus about 12,000 years ago," Simmons said. "This suggests that seafarers didn't need to have already domesticated plants and animals to go to these islands, which is a pretty complex set of tricks — they could have been hunter-gatherers."
Recently, research has hinted that seafarers may have made their way out to the Mediterranean islands even earlier, long before the Neolithic, and not only to isles close to the mainland, but to more distant ones as well, such as Crete.
For instance, stone artifacts on the southern Ionian Islands hint at human sites there as early as 110,000 years ago. Investigators have also recovered quartz hand-axs, three-sided picks and stone cleavers from Crete that may date back about 170,000 years ago. The distance of Crete about 100 miles (160 kilometers) from the mainland would have made such a sea voyage no small feat.
The exceedingly old age of these artifacts suggests the seafarers who made them might not even been modern humans, who originated between 100,000 and 200,000 years ago. Instead, they might have been Neanderthals or perhaps even Homo erectus.
"The whole idea of seafaring makes these extinct groups seem more human — they were going out to sea to explore places that were uninhabited," Simmons told LiveScience.
Dating artifacts
The problem with these ancient finds is determining their exact age. "They're well beyond the range of radiocarbon dating," Simmons said. Although researchers can also deduce the ages of artifacts based on the ages of surrounding materials, these artifacts weren't found in reliable contexts that could indisputably attest to their age, he added.
Although the idea that extinct human lineages possessed such advanced mental capabilities might be controversial, ancient seafaring has been seen elsewhere in the world. For instance, Australia was colonized at least 50,000 years ago, while fossils in Indonesia suggest that an extinct lineage of humans was seafaring as long ago as 1.1 million years.
"If the ancient finds in the Mediterranean can be verified, they will show that Homo erectus or Neanderthals or both had the skills and cognitive ability to build boats and navigate them," Simmons said.
Simmons detailed this research in the Nov. 16 issue of the journal Science.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus