World's Smallest Ear Can Hear Germs
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
A pin dropping is pretty quiet. But what about a bacterium?
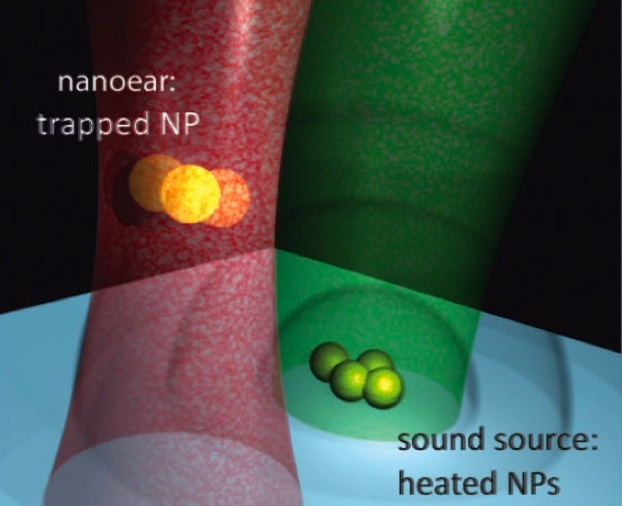
Hearing anything smaller than a certain size would ordinarily be tough to do. But not if you have "nano-ears." This kind of ear is a microscopic particle of gold trapped by a laser beam and can pick up sound a million times fainter than humans can usually hear.
BLOG: Video Hits a Trillion Frames Per Second
Sound waves happen when air is compressed and decompressed by pressure waves. Measuring that pressure — really measuring how air molecules are moving back and forth — one would see a sine wave pattern, and that is what makes sound of a given frequency.
To measure sound waves made at tiny scales, though, you need a way to measure movements at a similarly small scale, and no microphone can do that. That's where the gold particle and the laser beam come in.
The laser beam forms a pair of "optical tweezers" — a laser beam is focused by a lens and that beam can then move tiny particles around. It's a common method used in many areas of research in molecular biology.
In this case, optical physicist Jochen Feldmann and his colleagues in the Photonics and Optoelectronics Group at the University of Munich in Germany trapped a 60-nanometer wide gold particle with a laser. The gold particle was immersed in water surrounded by others like it. The scientists then heated the other nanoparticles with another laser, and measured how much the first one moved in response.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
BLOG: Is Star Trek's Tractor Beam Possible?
What they got was a way to hear vibrations with more sensitivity than ever before. They could even tell which direction the sound came from. A three-dimensional array could build an acoustic picture of a very small object.
So why care what a germ sounds like? There's some way to go before this becomes an experimental tool, but early indications are that it could be used to see microorganisms move in a way that hasn't been done before. If nothing else it opens up a whole new line of research, similar to the way ultrasound opened up prenatal care.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










