'Swarm of boulders' in space shows the gory aftermath of NASA's asteroid-smashing DART mission
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) has left a vast field of rubble strewn around asteroid Dimorphos, Hubble images show.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
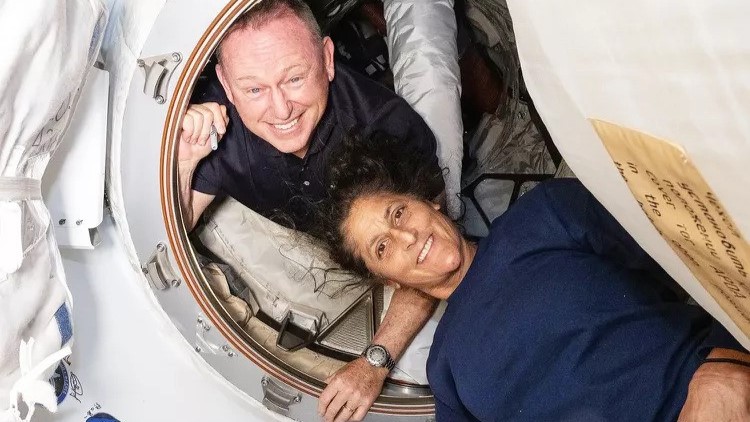
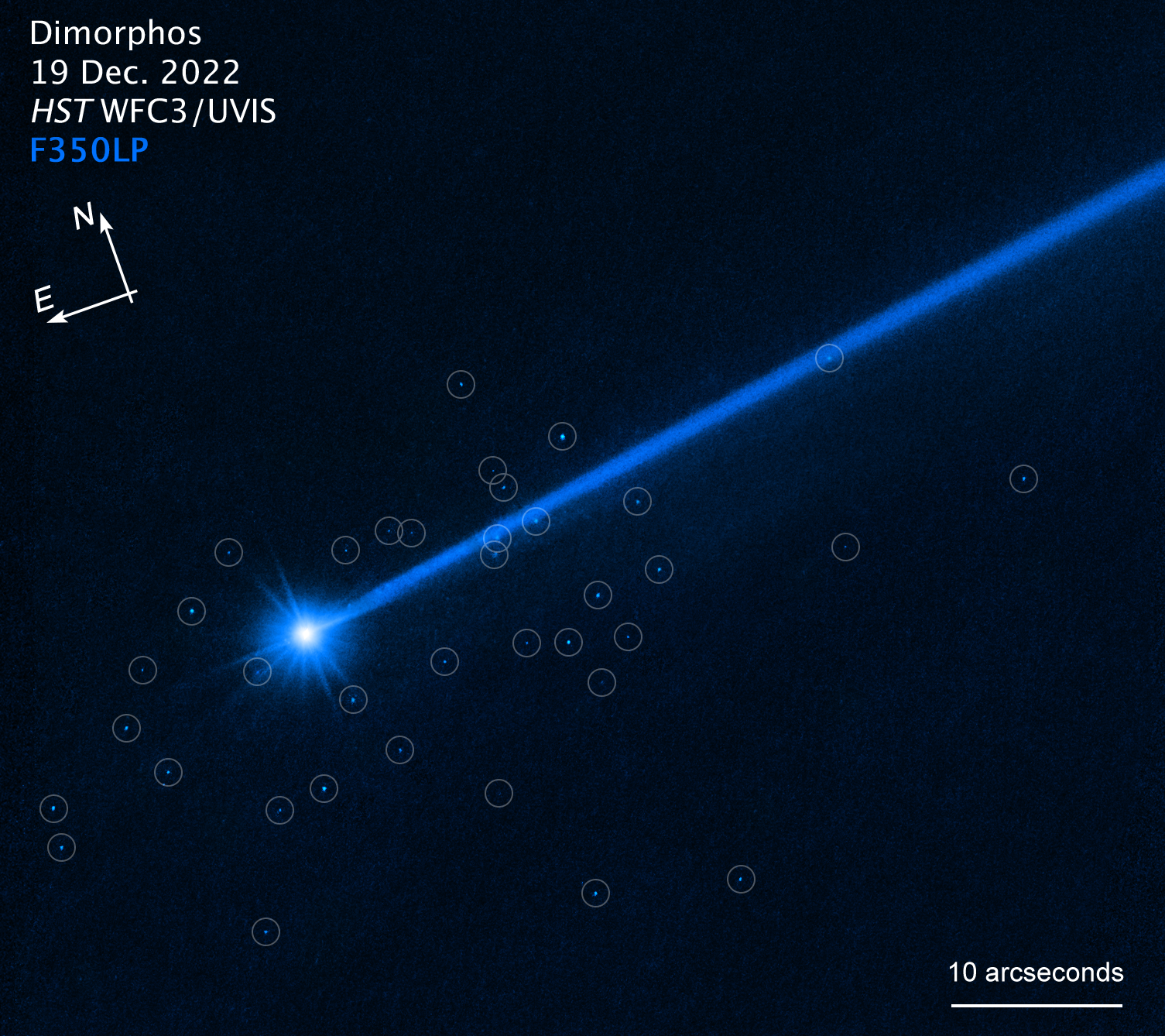
The Hubble Space Telescope has spotted the gory aftermath of the first-ever intentional collision between a spacecraft and an asteroid, revealing a debris field of at least 37 "boulders" flung thousands of miles into space.
On Sept. 26, NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft disintegrated as it smashed into the asteroid Dimorphos, which is 7 million miles (11 million kilometers) from Earth, successfully changing the asteroid's trajectory.
Now, by using Hubble to study the impact, astronomers have found that DART's roughly 14,540 mph (23,400 km/h) impact on the asteroid produced a "swarm of boulders." The rocks, which range from 3 to 22 feet (0.9 to 6.7 meters) in diameter, were most likely shaken loose from the asteroid's surface during the impact. The researchers published their findings July 20 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Related: NASA confirms success of DART mission, proving humanity can deflect killer asteroids with rockets
"This tells us for the first time what happens when you hit an asteroid and see material coming out up to the largest sizes," David Jewitt, a planetary scientist at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in a statement. "The boulders are some of the faintest things ever imaged inside our solar system."
DART's goal was to change the orbit of Dimorphos around its larger partner — the 2,560-foot-wide (780 m) asteroid Didymos — by at least 73 seconds. However, the spacecraft widely exceeded that target, altering Dimorphos' orbit by a whopping 32 minutes.
This means the 1,210-pound (550 kilograms), $314 million DART spacecraft — a squat, cube-shaped probe that consisted of sensors, an antenna, an ion thruster and two 28-foot-long (8.5 m) solar arrays — pushed Dimorphos closer to Didymos and shortened the smaller asteroid's orbital path. The mission's success raises the odds that a method like this could one day be used to nudge a harmful asteroid away from a deadly collision course with Earth.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The boulders, which make up an estimated 0.1% of Dimorphos' mass, were spotted drifting away from the asteroid at just over a half mile per hour (0.8 km/h) — "roughly the walking speed of a giant tortoise," according to NASA.
"This is a spectacular observation — much better than I expected," Jewitt said. "We see a cloud of boulders carrying mass and energy away from the impact target… If we follow the boulders in future Hubble observations, then we may have enough data to pin down the boulders' precise trajectories. And then we'll see in which directions they were launched from the surface."

Ben Turner is a U.K. based writer and editor at Live Science. He covers physics and astronomy, tech and climate change. He graduated from University College London with a degree in particle physics before training as a journalist. When he's not writing, Ben enjoys reading literature, playing the guitar and embarrassing himself with chess.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus