Surges of activity in the dying human brain could hint at fleeting conscious experiences
An increase in a certain kind of high-frequency wave in dying brains might be associated with last-minute conscious experiences, but scientists don't know for sure.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
In their last minutes of life, some people's brains generate a surge of surprisingly organized-looking electrical activity that may reflect consciousness — although scientists aren't entirely sure.
According to new research, published Monday (May 1) in the journal PNAS, this surge can sometimes occur after a person's breathing stops but before the brain stops functioning. The activity pattern is somewhat similar to what is seen when people are awake or in dreamlike states, leading to speculation that perhaps these electrical surges reflect the otherworldly experiences reported by people who've had close brushes with death: A sense of looking at the body from the outside; a tunnel and white light; or a sense of reliving important memories.
However, since all the patients in the new study ultimately died, it's impossible to know if they had such experiences.
"If you talk about the dying process, there is very little we know," said Jimo Borjigin, a neuroscientist at the University of Michigan Medical School who led the study. It's rare for patients to have their brains continuously monitored as they die, Borjigin told Live Science. "This is maybe the first study to really show second-by-second how the brain dies."
Related: Is brain death reversible?
Near-death experiences
Some people who are brought back from the brink of death report seeing or hearing unexplained things during resuscitation or when they seem to be unconscious. The reason for these near-death experiences is unknown, and it's not clear if they're even specific to death.
International surveys suggest that only about half of what people call "near-death experiences" actually occur in life-threatening situations, said Daniel Kondziella, a neurologist at the University of Copenhagen who was not involved in the new research. The other half occur during meditation or in scary situations that don't endanger one's health or impact the brain's metabolism, Kondiziella told Live Science.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"The thing is, from the experience itself you cannot say if someone has had a cardiac arrest or syncope [a brief loss of consciousness] or near-miss traffic accident," Kondiziella said.
Because the people who survive to report a near-death experience are inherently different from the people who die — their brains don't permanently lose function, for one thing — it's hard to determine whether those who actually die also have these subjective experiences.
In 2013, Borjigin and her colleagues measured electrical activity in the brains of rats that they euthanized via cardiac arrest. They found that for about 30 seconds after the heart stopped, the brain showed a surge in what are called gamma waves, which are the highest-frequency electrical oscillations in the brain. Gamma waves are correlated with conscious experience, but don't necessarily prove that someone is conscious; they're just one of many indicators that someone might be aware and alert.
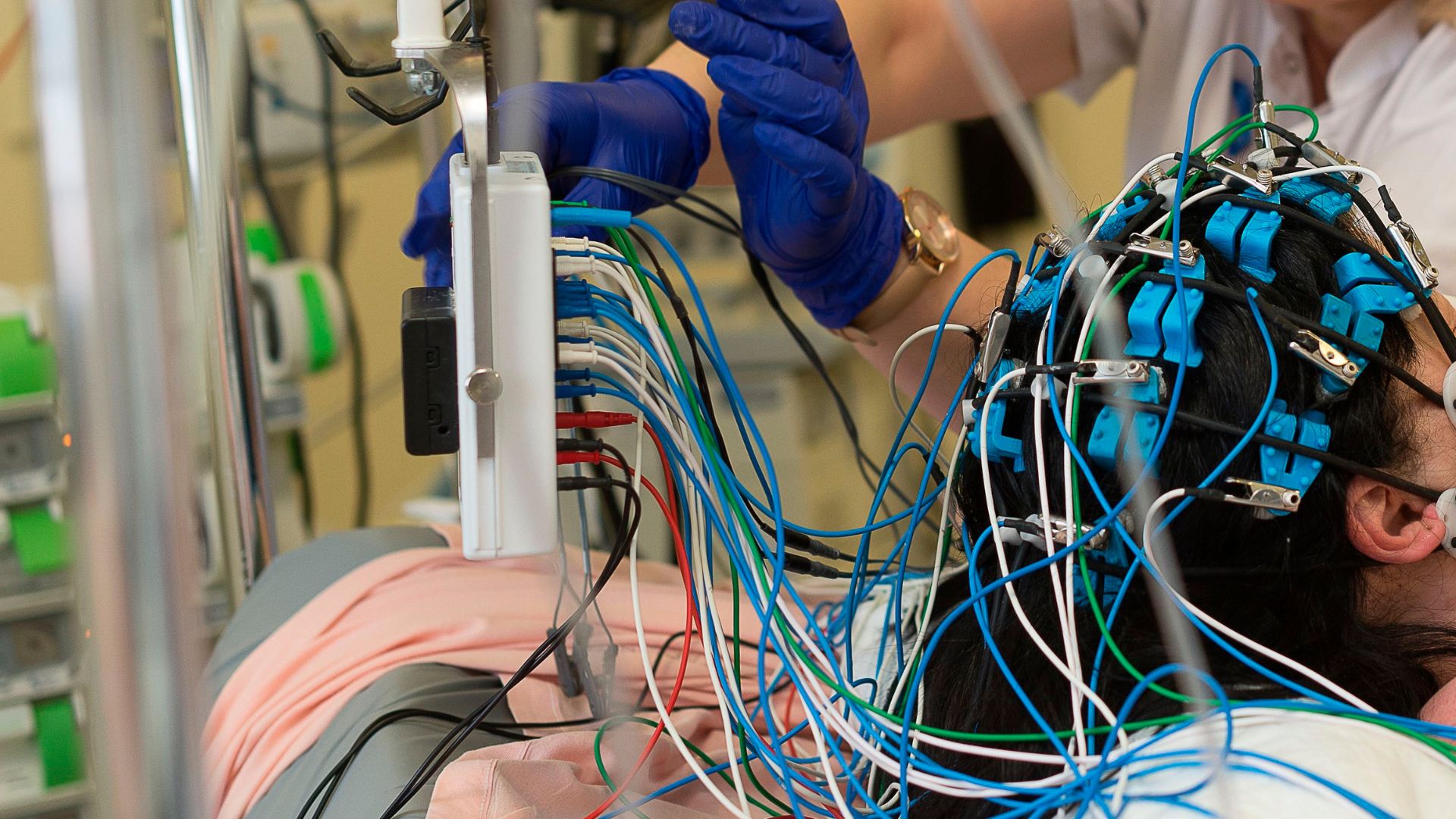
In 2022, a separate group of doctors happened to be monitoring the brain of an 87-year-old man with an electroencephalogram (EEG), which detects electrical activity on the surface of the brain, when the man unexpectedly died. Similar to Borjigin's rats, the man's brain showed a surge in gamma activity in the 30 seconds before and after his heart stopped.
'Reading' the dying brain
In their new paper, Borjigin and her team made a deliberate effort to use EEG to capture what the brain looks like during death.
The researchers got permission to monitor dying patients in intensive care whose breathing support had been removed after treatment proved futile. The study included four patients total, all of whom were comatose after cardiac arrest.
In the 30 seconds to two minutes after their ventilators were removed, two of the four patients' brains showed surges in gamma waves. Interestingly, this gamma activity seemed organized, in that the gamma waves in one portion of the brain were associated with predictable activity patterns in other regions.
The temporoparietal junction, a brain region where the temporal and parietal lobes meet, toward the back of the brain behind the ear, was particularly active with gamma waves. This region is known to be activated when people have out-of-body experiences or dreams, Borjigin said.
The new findings echo what was seen in the 87-year-old patient who unexpectedly died, said Raul Vicente, a neuroscientist and data scientist at the University of Tartu who co-authored the 2022 study but was not involved in Borjigin's work. "It's very nice to see a confirmation," he told Live Science.
"The more consistent findings we have, the more evidence it is that this likely is a mechanism happening at the time of death and if we can pinpoint this down to one location, even better," said Ajmal Zemmar, a neurosurgeon at the University of Louisville Health who also co-authored the 2022 study.
Zemmar and Vicente are optimistic that these signals could be signs of conscious experience at the moment of death. But reflecting the debate in the field, Kondziella is more skeptical.
"We know when you die a cardiac death as opposed to a brain death, that takes time," he said. Minutes pass between the heart stopping and brain cells dying, he said. "It shouldn't be a big surprise during those minutes, you will see aberrant electrophysiological activity in the brain."
Some people may experience something like near-death experiences in these moments, Kondziella said, but we may never know for sure. And again, these experiences may not be unique to death — a more likely explanation for near-death experiences that encompasses both life-threatening experiences and non-life-threatening experiences, he said, may be "REM sleep intrusion into wakefulness," a situation in which the brain blends waking and dreaming states. (REM sleep is marked by dreaming and brain activity patterns that are very similar to waking, including gamma waves and other, lower-frequency waves.)
Borjigin's team is still collecting end-of-life data, hoping to add to the evidence that the dying brain may generate predictable gamma-wave patterns. Already, other research groups have attempted to use artificial intelligence to identify objects that people saw in their dreams based on their brain activity — similar mind-reading may be possible with unconscious and dying patients, Vicente said.
"This opens an opportunity at some point, if we gather enough data, to be able to decode what people in different coma states are thinking," Vicente said.

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










