Chemo side effect caused man's eyelash growth to go haywire
Some medicines can inadvertently cause people's eyelashes to grow incredibly long.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
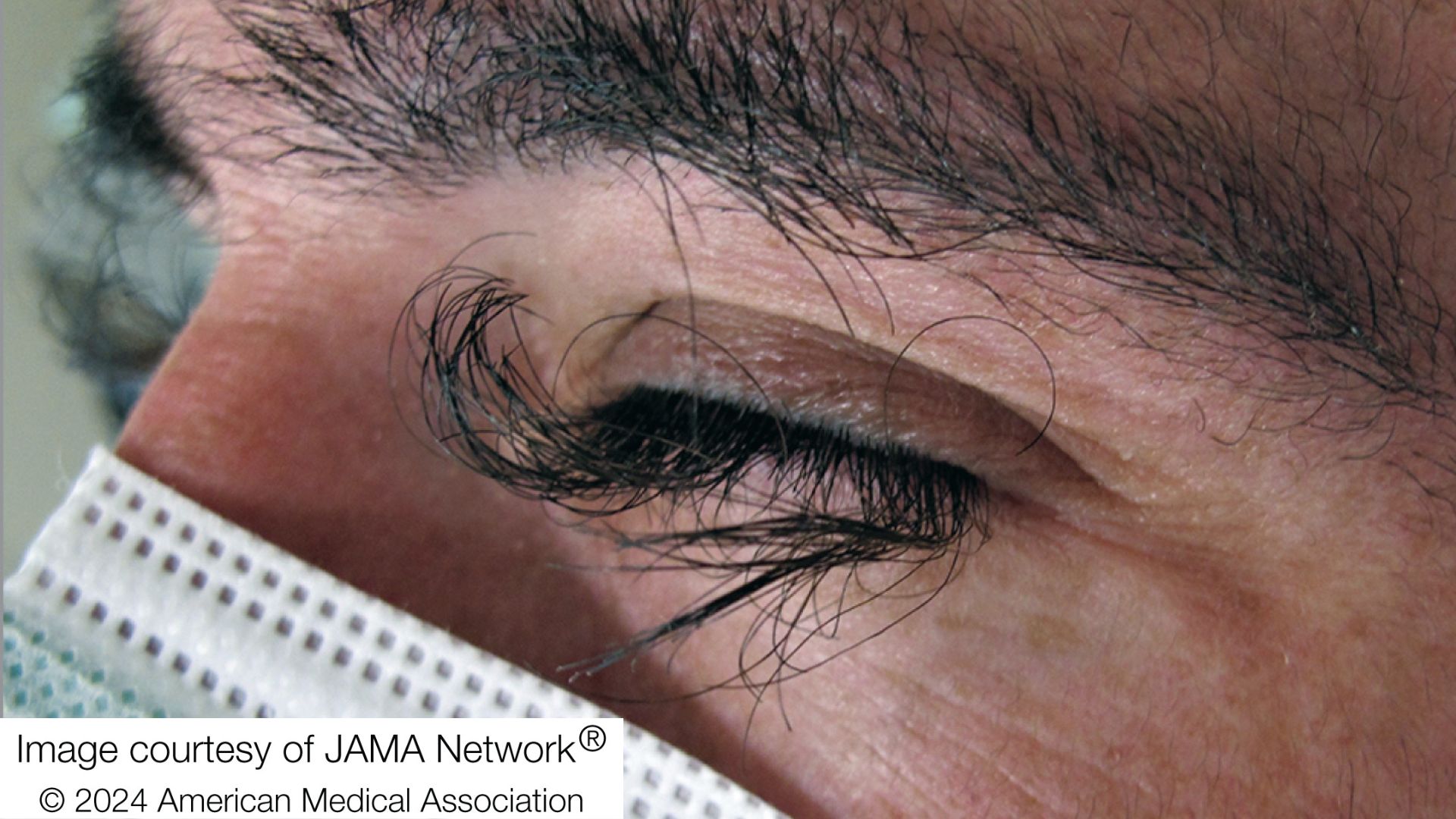
A man's eyelashes grew unusually long and developed a dramatic curl — and it turned out to be a side effect of his cancer treatment.
In a report of the man's case, published Wednesday (April 24) in the journal JAMA Dermatology, doctors called the patient's sudden eyelash growth "drug-induced trichomegaly." Trichomegaly refers to a condition in which eyelashes grow very, very long, usually exceeding their usual length by about 0.5 inch (12 millimeters) or more. At the same time, the eyelashes can become curlier, thicker and darker.
Several drugs can trigger trichomegaly, including a class of medicines known as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors. These include a chemotherapy drug called panitumumab, which works by blocking EGFR in the body; the man was taking this drug as part of a chemotherapy regimen for advanced colorectal cancer. By blocking the receptor on tumor cells, the drug increases the chances that the cells will self-destruct and also suppresses their ability to grow and spread.
However, EGFR isn't unique to cancer cells. The receptors appear in high quantities in certain types of tumors, but they are also found in healthy tissues, including cells found in the outer layer of the skin and in hair follicles.
Related: Why do we have eyebrows and eyelashes?
Evidence suggests that blocking EGFR may throw off the normal cycle of hair growth, extending the stage in which hair actively grows. Turning down EGFR has also been tied to an increase in hair coarseness and curliness, as well as to the formation of new hair follicles. The resulting, haywire eyelash growth is well established as a potential side effect of EGFR blockers, having been reported alongside striking images in other medical journals in the past.
In addition to chemotherapy drugs like panitumumab, other medicines can trigger trichomegaly. For instance, prostaglandins — hormone-like drugs used to treat glaucoma, among other conditions — are thought to boost eyelash growth in a similar way to EGFR blockers.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The condition has also been tied to infections such as HIV/AIDS and to various genetic syndromes, including ones that affect the response to growth factors.
When panitumumab triggers eyelash growth, the side effect normally shows up within the first few months of a person starting treatment and goes away after the treatment stops, the report authors noted. In the man's case, he was simply given "detailed instructions regarding safe eyelash trimming" to deal with his extra-long lashes.
Trichomegaly is usually harmless, except in cases where the eyelashes start to grow in the wrong direction, toward the eyeball. This is known as trichiasis, and it can damage the outer layer of the eye and lead to ulcers, vision loss and, in severe cases, blindness.
Ever wonder why some people build muscle more easily than others or why freckles come out in the sun? Send us your questions about how the human body works to community@livescience.com with the subject line "Health Desk Q," and you may see your question answered on the website!

Nicoletta Lanese is the health channel editor at Live Science and was previously a news editor and staff writer at the site. She holds a graduate certificate in science communication from UC Santa Cruz and degrees in neuroscience and dance from the University of Florida. Her work has appeared in The Scientist, Science News, the Mercury News, Mongabay and Stanford Medicine Magazine, among other outlets. Based in NYC, she also remains heavily involved in dance and performs in local choreographers' work.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










