Man Coughs Up a Giant Blood Clot in the Shape of His Lung
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
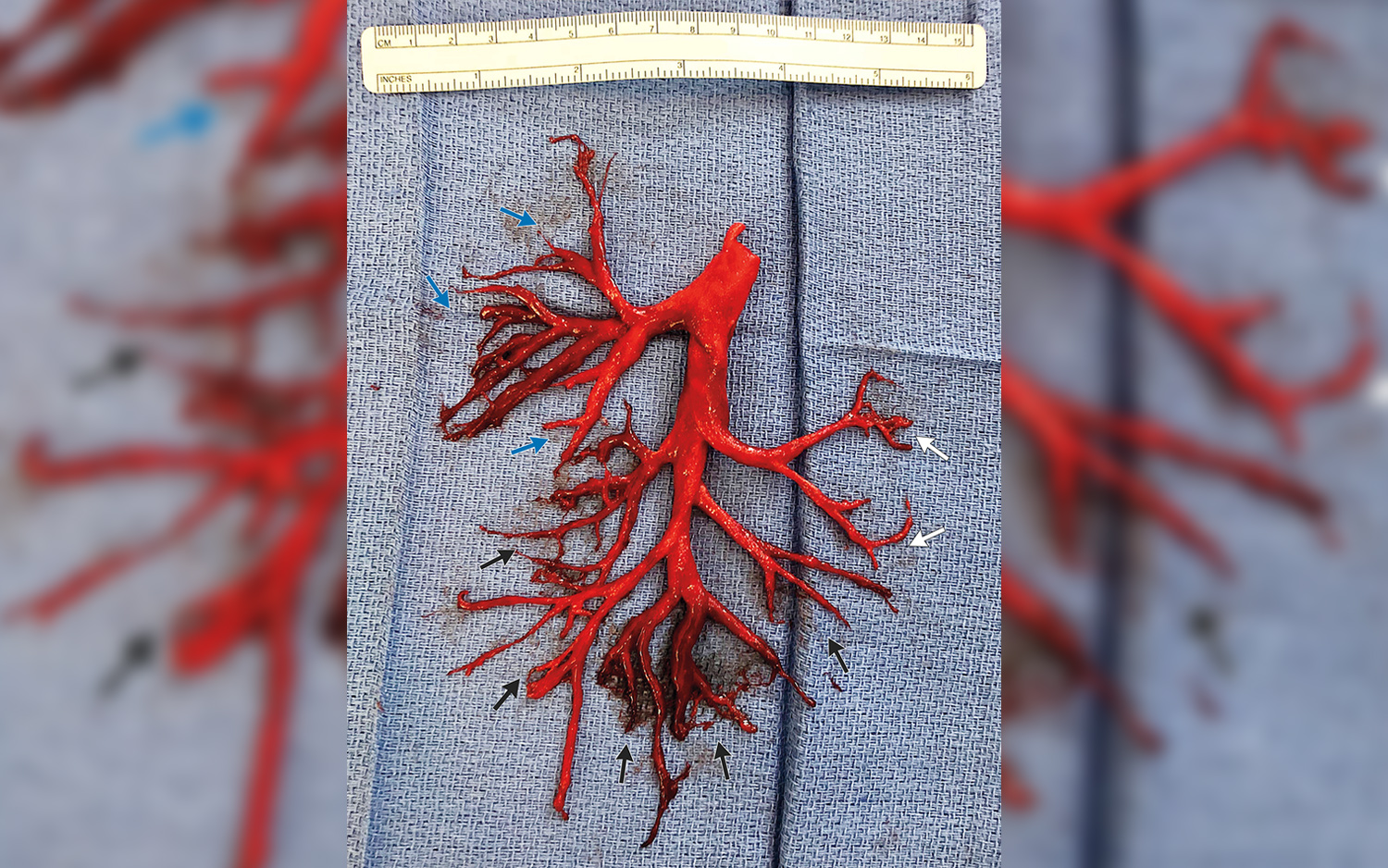
Coughing up blood is an alarming symptom, but it's not particularly rare. Even so, one man in California shocked his doctors when he coughed up an unusual-looking blood clot: It was in the shape of his lung.
The 36-year-old man was being treated for a serious heart condition, according to a new report of the case, published Nov. 29 in The New England Journal of Medicine. He had chronic heart failure, which means the heart muscle can't pump enough blood to meet the body's normal demands.
His condition was so severe that doctors put him on a machine called a ventricular assist device, which helps the heart pump blood. Because these machines can also increase the risk of blood clots, he was prescribed a blood-thinner medication.
However, these medications also increase the risk of bleeding, including coughing up blood. Indeed, the patient had several coughing episodes in which he expelled small amounts of blood, according to the report. But then, during an "extreme bout of coughing," the patient spit out an "intact cast" of the right bronchial tree. In other words, it was a mold (cast) made of clotted blood in the shape of the lung's branched airway passages known as bronchi.
"We were astonished," Dr. Georg Wieselthaler, a heart and lung surgeon at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), who treated the patient, told The Atlantic. "It's a curiosity you can't imagine — I mean, this is very, very, very rare."
It's less rare for patients to cough up bronchial "casts" made of other substances, such as lymph or mucus. But blood is less sticky and sturdy than these other substances, meaning that a cast made of blood is less likely to hold together when coughed up, The Atlantic reported.
Wieselthaler told The Atlantic that in this case, the patient had an infection that increased levels of a protein called fibrinogen, which helps blood clots form; and higher levels of fibrinogen could have helped the man's large clot to stay intact when it was coughed up.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Even though the man had no further episodes of coughing up blood, he unfortunately died a week later from complications of heart failure.
Wieselthaler's colleague, Dr. Gavitt Woodard, a clinical fellow at UCSF, told The Atlantic that one reason they decided to publish the image was to show the "beautiful anatomy of the human body."
- 11 Surprising Facts About the Respiratory System
- 12 Amazing Images in Medicine
- 27 Oddest Medical Cases
Originally published on Live Science.

Rachael is a Live Science contributor, and was a former channel editor and senior writer for Live Science between 2010 and 2022. She has a master's degree in journalism from New York University's Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program. She also holds a B.S. in molecular biology and an M.S. in biology from the University of California, San Diego. Her work has appeared in Scienceline, The Washington Post and Scientific American.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










