In Photos: Bizarre Parasites From the Past
Jurassic Amphibian

A 165-million-year-old fossil of a fly larva, now dubbed Qiyia jurassica would have latched onto Jurassic salamanders and other amphibians with a mid-body sucker before using its piercing mouthparts to suck its host's blood.
Fine-grained mudstone
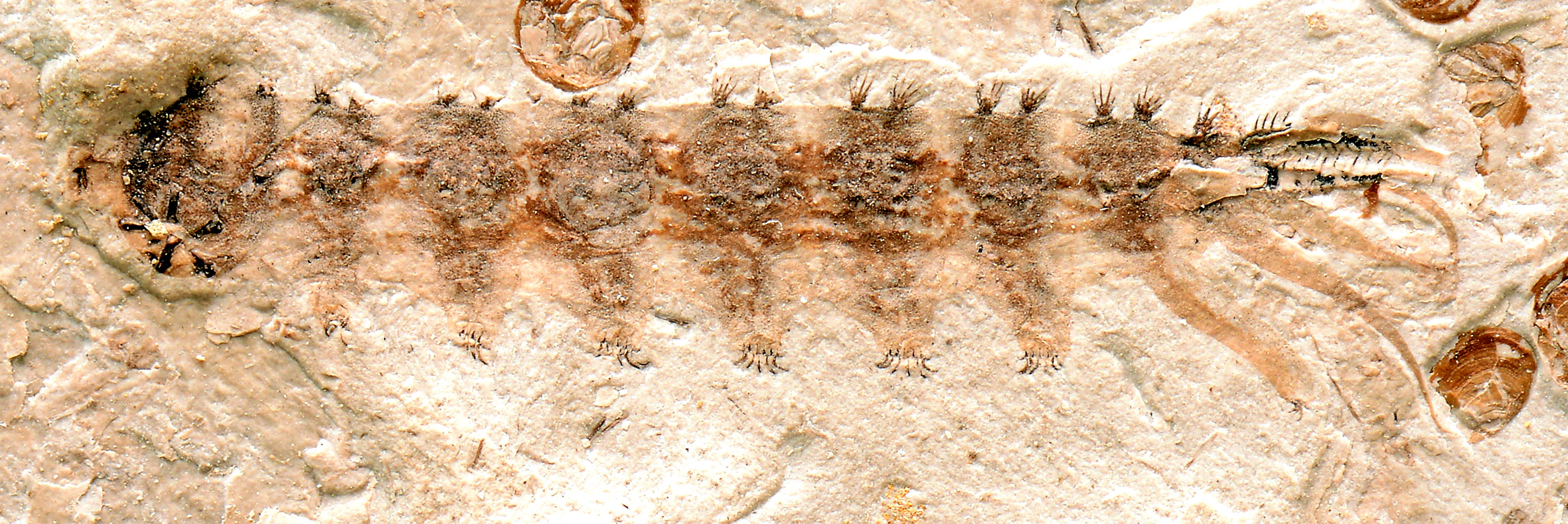

The fine-grained mudstone in which the fossil fly larva was found near Ningcheng in Inner Mongolia preserved several details of the parasite's body, including soft tissue, the thoracic sucker plate, fine setae and its piercing mouthparts.
Bizarre Parasite
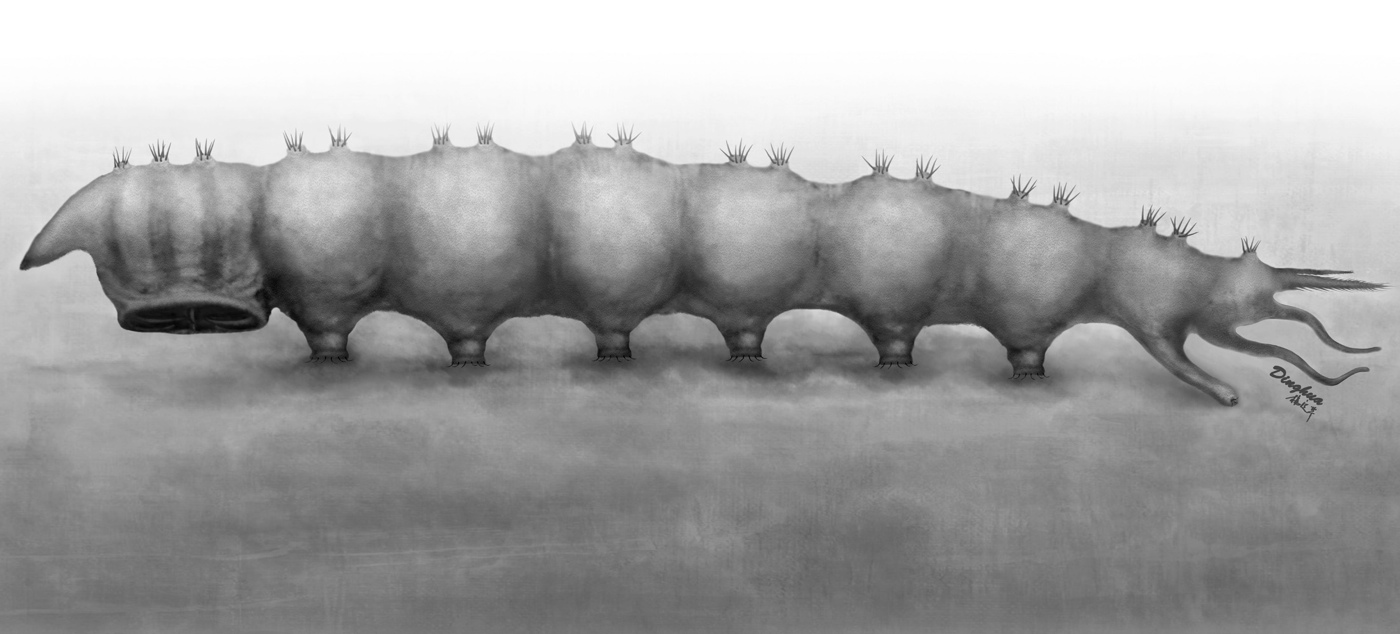

The fly larva, Qiyia jurassica was wild-looking. It sported a tiny, tube-shaped head tipped with piercing mouthparts for bloodsucking, a sucker plate beneath its mid-body (thorax) and caterpillarlike hindlegs.
Jurassic Fleas
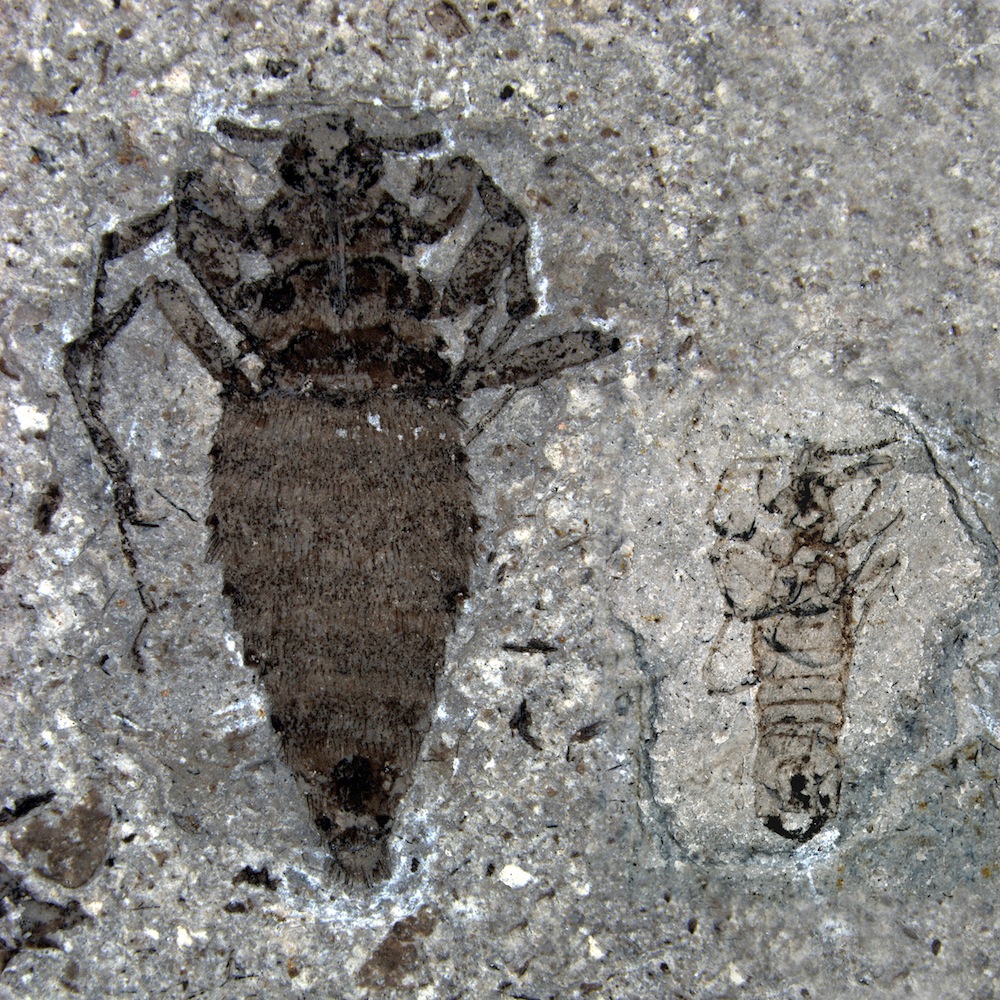

This fly larva is one of several ancient parasites with wild looks and lifestyle. For instance, the oldest know fleas, which belonged to the Pseudopulicidae genus, lived 165 million years ago in what is now northeastern China. The Pseudopulicidae bloodsuckers were five to 10 times bigger than today's fleas and may have sucked the blood of dinosaurs, researchers said. Here, a female (left) and male (right) flea from the middle Jurassic in China.
Ancient Bloodsucker
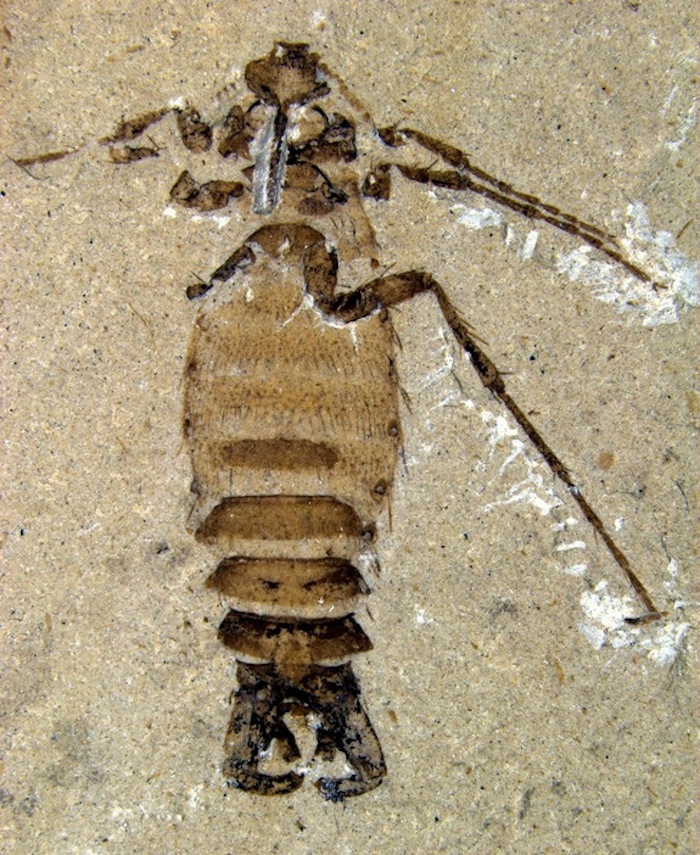

The fossilized remains of the oldest known fleas were found in China. These ancient bloodsuckers, in the genus Pseudopulicidae, lived 250 million years ago to 65 million years ago.
The ancient fleas were five to 10 times larger than today's fleas, but lacked the strong hindlegs of their modern counterparts.
Fossilized Flea Unearthed in China
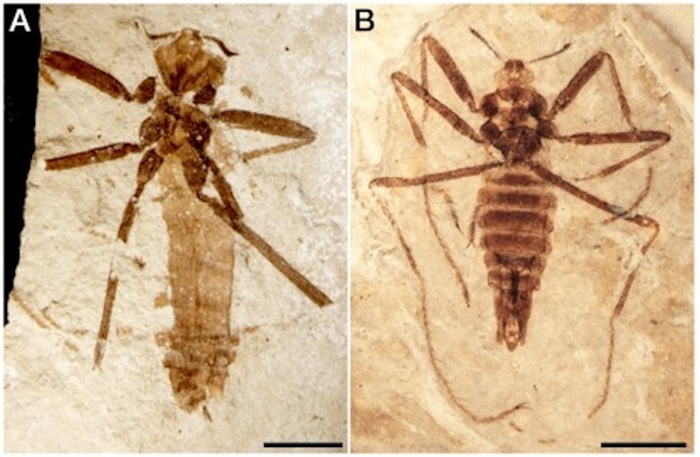

This ancient parasite (Saurophthyrus exquisitus) was discovered in sediments in northeastern China. The 125-million-year-old flea's body measures 0.8 inches (2 centimeters), making it smaller than older pests, but larger than modern-day fleas.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Jeanna Bryner is managing editor of Scientific American. Previously she was editor in chief of Live Science and, prior to that, an editor at Scholastic's Science World magazine. Bryner has an English degree from Salisbury University, a master's degree in biogeochemistry and environmental sciences from the University of Maryland and a graduate science journalism degree from New York University. She has worked as a biologist in Florida, where she monitored wetlands and did field surveys for endangered species, including the gorgeous Florida Scrub Jay. She also received an ocean sciences journalism fellowship from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. She is a firm believer that science is for everyone and that just about everything can be viewed through the lens of science.