
Satellite Spies White Cliffs, Blue Waters of Dover
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
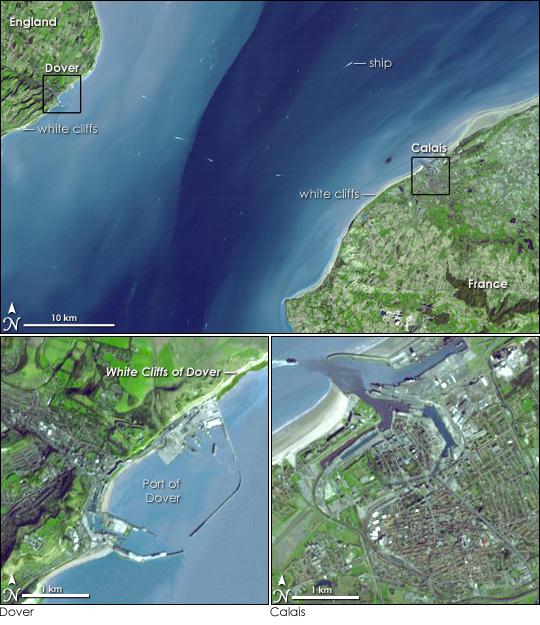
The strong pull of tidal currents sweeps water from the North Sea and the Atlantic Ocean through the narrow Strait of Dover. Resembling water-marked taffeta, the fast-moving water is streaked white, pale blue, turquoise, and royal blue in this image, taken by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA's Terra satellite on March 14, 2001.
The water is colored by the characteristic white chalk that forms the soil of this region. The white, chalky soil reflects light, giving the water its pale color near shore.
Aside from the color of the water, the chalk is evident along the shoreline, where tall, white cliffs rise on both the English and French side of the channel. On the British side, these geological formations are the famous White Cliffs of Dover.
Article continues belowThe Strait of Dover forms the narrowest part of the English Channel, where a scant 33 kilometers (20 miles) separates Great Britain from the rest of Europe. Because of the narrowness of the channel and its position as the gateway between the North Sea and the open Atlantic, the strait is very busy with ship traffic. Approximately 400 commercial vessels pass through the strait every day, says the Channel Navigation Information Service, making the Dover Strait one of the busiest waterways in the world.
Boats, traveling both north and south between Great Britain and France, and east and west between ocean and sea, trail white streaks behind them in this image. Car, train, and bus traffic also travel this path. The Channel Tunnel cuts beneath the water, connecting Dover, England with Calais, France.
- 7 Most Dangerous Places on Earth
- NASA to Go Boldly ... to the Arctic, Again
- 10 Biggest Volcanic Eruptions in History
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus











