New Look at Earth's Mysterious Layer

A mysterious layer lies beneath Earth's massive tectonic plates.
Sandwiched between two rock layers — the rigid lithosphere and the more pliable asthenosphere— this thin boundary is like the jelly in a peanut butter sandwich. Scientists think it could be very wet rock, or even partially melted rock, but no one knows for sure.
"There have been a lot on conflicting studies," said Kerry Key, a seismologist at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in San Diego.
Understanding the nature of the boundary layer and its role in plate tectonics is one of the grand challenges in seismology, according a list assembled by the Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology in 2009.
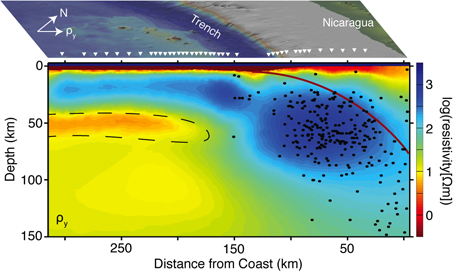
Now, a new study co-authored by Key appears to confirm the boundary zone is molten magma, at least under the ocean floor. Off the coast of Nicaragua, beneath the Cocos tectonic plate, researchers discovered a 15-mile-thick (25 kilometers) layer of partially melted rock at the bottom of the lithosphere. The results are published today (March 20) in the journal Nature.
"It's really a surprise," said Samer Naif, a Scripps graduate student and lead author of the study."We went out to try and understand the crustal fluid cycle at a subduction zone and we stumbled upon a partial-melt layer."
In past decades, the dominant view was that the boundary layer was likely melt-free, but weakened by water-rich minerals, Naif said. But in the last five years, new studies based on earthquake waves passing through the layer suggested the zone was molten, at least in certain places, he said.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The researchers saw the molten zone beneath the Cocos plate while using a technique that looks for subtle variations in Earth's naturally occurring electric and magnetic fields. These variations reveal structures below the surface, and are particularly effective at revealing pockets of liquid, such as oil and gas reservoirs.
"We've come out of left field with electromagnetic data, which shows much more sensitivity to features like this," Naif said. We could potentially have a lot more to say [about the boundary layer] if we go out and do more surveys," he told OurAmazingPlanet.
The lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB) puts the "plate" in plate tectonics, marking the bottom of the stiff tectonic plates that shift on Earth's surface, riding convection currents deeper in Earth's mantle. Both layers are solid rock, but the lithosphere is hard, stiff and cold and the hotter asthenosphere flows and deforms on a geologic time scale. The discontinuity, molten or not, lies at depths from 30 miles (50 km) under the ocean floor to 120 miles (200 km) beneath continents.
The group's next step is to explain why the magma is there, Key said. Other studies suggest that older ocean lithosphere does not have a molten LAB, Naif added. The geologically young Cocos plate could have remnant magma plastered to its underbelly from its birth at a nearby mid-ocean spreading ridge, for example.
Email Becky Oskin or follow her @beckyoskin. Follow us @OAPlanet, Facebook or Google+. Original article on LiveScience's OurAmazingPlanet.




