Major Earthquakes Can Trigger Faraway 'Slow' Quakes
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Major earthquakes might set off incredibly slow earthquakes thousands of miles away, new research suggests.
These findings, detailed online Sept. 11 in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth,shed light on how earthquake zones might communicate with each other over large distances, scientists added.
The cluster of devastating earthquakes that rocked the globe during the past decade from Japan to Sumatra to Haiti is one reason why scientists are investigating whether temblors in different parts of the world are linked to one another. Although research to date suggests that major quakes aren't likely to trigger other massive quakes around the globe, they can set off tremors worldwide.
Now researchers find that large quakes might also trigger mysterious slow earthquakes thousands of miles away. One kind of slow earthquake known as a slow-slip event can last for weeks, shifting the Earth as much as an ordinary earthquake of magnitude of 7 would in mere moments.
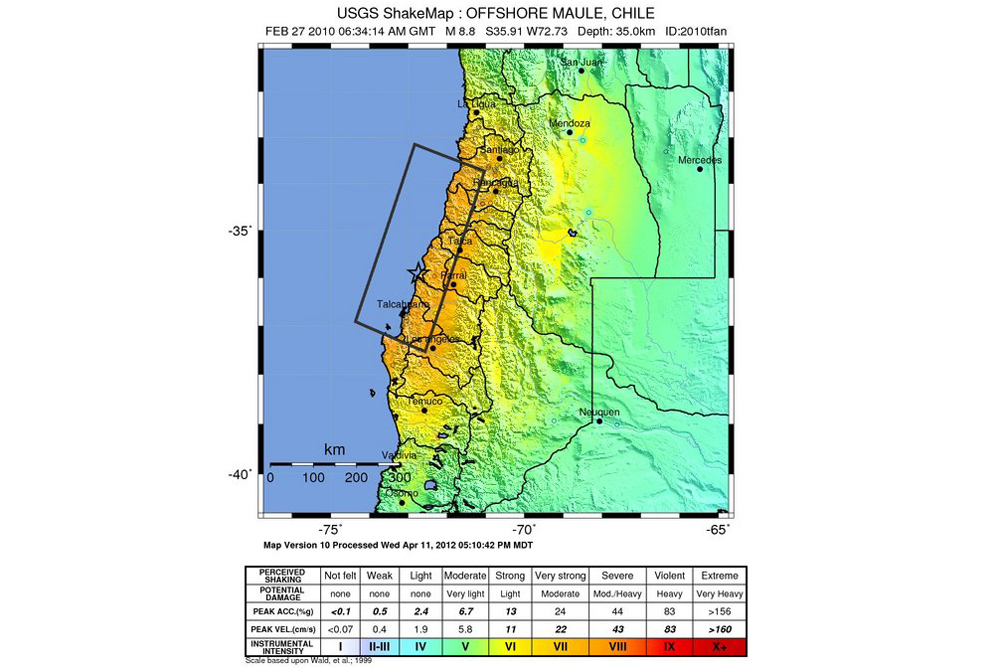
The investigators focused on the magnitude 8.8 Maule earthquake that struck Chile in 2010. They found it generated surface waves that, within hours, set off tremors in the Guerrero region of southwestern Mexico 4,140 miles (6,660 kilometers) away. Data from GPS stations also revealed the earth there began moving southward at the same time tremors there began.
The tremors and movements of the GPS stations lasted for about six months after the 2010 Chile quake.
"Such an observation may indicate that the Maule earthquake triggered a slow-slip event in Guerrero," said researcher Dimitri Zigone, a seismologist at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Near Guerrero lies a subduction zone, where a tectonic plate under the Pacific Ocean is diving under the continental North American plate. The seismic energy from Chile apparently increased the stress in the segment of the subduction zone near Guerrero, which may explain the resulting slow-slip event.
"The fact large quakes can have effects so far away could be important because it may change the recurrence time between earthquakes in a specific location," Zigone told OurAmazingPlanet. "Usually we assume that the seismic cycle — the recurrence between earthquakes — is regional, on a single fault system orat a plate boundary, for example. If these large-scale interactions exist, it may indicate that even at large distances, a mega-earthquake can modify the conditions in another region."
This story was provided by OurAmazingPlanet, a sister site to LiveScience. Follow OurAmazingPlanet for the latest in Earth science and exploration news on Twitter @OAPlanet. We're also on Facebook & Google+.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus