Supercomputer Recreates Universe From Big Bang to Today
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Scientists would love to be able to rewind the universe and watch what happened from the start. Since that's not possible, researchers must create their own mini-universes inside computers and unleash the laws of physics on them, to study their evolution.
Now researchers are planning the most detailed, largest-scale simulation of this kind to date. One of the main mysteries they hope to solve with it is the origin of the dark energy that's causing the universe to accelerate in its expansion.
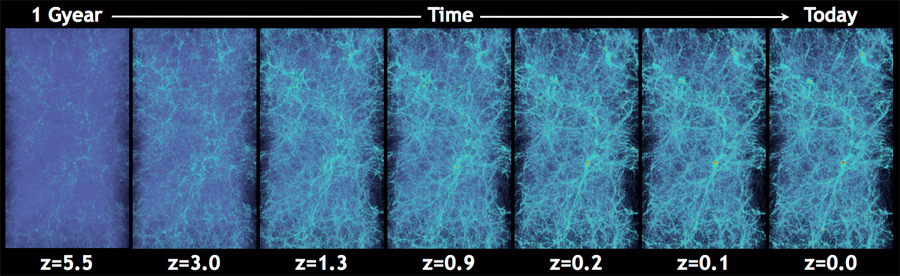
The new simulation is a project led by physicists Salman Habib and Katrin Heitmann of Illinois' Argonne National Laboratory, and will run on the lab's Mira supercomputer, the third-fastest computer in the world, starting in the next month or two. The program will use hundreds of millions of "particles" — elements in the simulation that stand in for small bits of matter. The computer will let time run, and watch as the particles move through space in response to the forces acting on them.
As the simulation progresses, these bits of matter will clump together under gravity to form larger and larger blobs representing galaxies, galaxy clusters and superclusters. To evolve the universe from the Big Bang 13.7 billion years forward to today, the simulation will take up to two weeks. [Video: Simulation of the Universe from Big Bang to Now]
Testing the theory
The ultimate goal is to compare the best telescope observations of structure in the universe to the structure displayed in the computer model, to test the reigning theory of cosmology.
"We are trying to look for subtle ways in which it's wrong," Habib told SPACE.com. "That’s why you need these very high-resolution, very large-scale simulations to see if the observations don't match the predictions."
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Dark energy is the name given to whatever is causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate. When this acceleration was first discovered in the 1990s, it shocked the science community, because theories predicted the universe's expansion would be steady or slowing down, because of the inward pull of gravity.
The current reigning theory posits that dark energy is what's called the cosmological constant, a term Einstein first thought to put into his equations of general relativity to represent the vacuum energy of the universe. Although Einstein ultimately decided not to include the term, scientists later realized that it could explain the current observations of the expansion of the universe.
However, cosmologists aren't satisfied with this explanation, Habib said.
Another possibility
"It's just a single number entered as an extra term in the equations," he said. "The problem is that if you ask what its value should be, it's enormous — many orders of magnitude bigger than what is actually observed."
While simulations based on the cosmological constant so far appear to match what's seen in large-scale observations of the universe, scientists think that next-generation observations may reveal discrepant details.
If a cosmological constant is not to blame for the accelerated expansion of the universe, another possibility is that space contains some other type of mass or energy, such as a field, that is pulling everything apart.
"It's basically guesswork; it could be like this, or it could be like that," Habib said. "Either way it's very interesting."
Follow Clara Moskowitz on Twitter @ClaraMoskowitz or SPACE.com @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook & Google+.

Tariq is the editor-in-chief of Live Science's sister site Space.com. He joined the team in 2001 as a staff writer, and later editor, focusing on human spaceflight, exploration and space science. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times, covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. He is also an Eagle Scout (yes, he has the Space Exploration merit badge) and went to Space Camp four times. He has journalism degrees from the University of Southern California and New York University.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus











