Did Shroud of Turin Inspire Spread of Christianity?
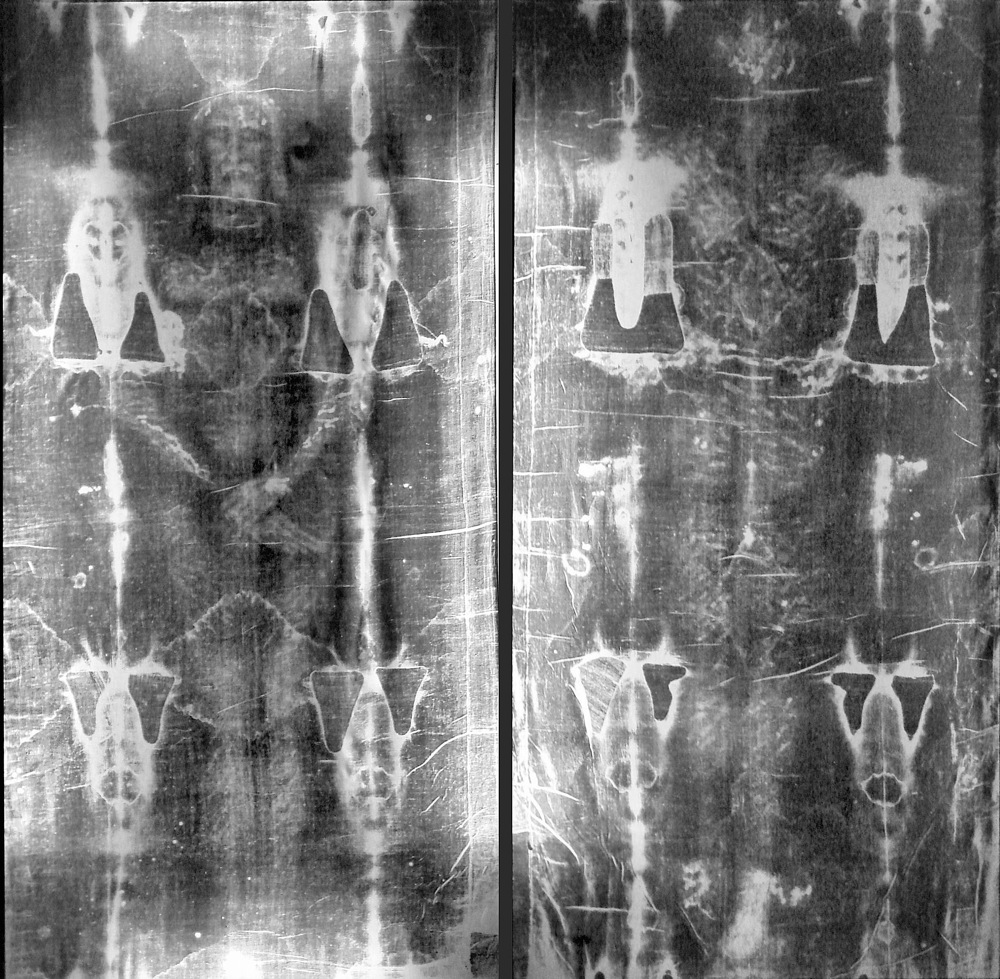
A hoax or a miracle? The Shroud of Turin has inspired this question for centuries. Now, an art historian says this piece of cloth, said to bear the imprint of the crucified body of Jesus Christ, may be something in between.
According to Thomas de Wesselow, formerly of Cambridge University, the controversial shroud is no medieval forgery, as a 1989 attempt at radiocarbon dating suggests. Nor is the strange outline of the body on the fabric a miracle, de Wesselow writes in his new book, "The Sign: The Shroud of Turin and the Secret of the Resurrection" (Dutton Adult, 2012). Instead, de Wesselow suggests, the shroud was created by natural chemical processes — and then interpreted by Jesus' followers as a sign of his resurrection.
"People in the past did not view images as just the mundane things that we see them as today. They were potentially alive. They were seen as sources of power," de Wesselow told LiveScience. The image of Jesus found on the shroud would have been seen as a "living double," he said. "It seemed like they had a living double after his death and therefore it was seen as Jesus resurrected."
Believing the shroud
As de Wesselow is quick to admit, this idea is only a hypothesis. No one has tested whether a decomposing body could leave an imprint on shroud-style cloth like the one seen on the shroud. A 2003 paper published in the journal Melanoidins in Food and Health, however, posited that chemicals from the body could react with carbohydrates on the cloth, resulting in a browning reaction similar to the one seen on baked bread. (De Wesselow said he knows of no plans to conduct an experiment to discover if this idea really works.)
Perhaps more problematic is the authenticity of the shroud itself. Radiocarbon dating conducted in 1988 estimated the shroud to medieval times, between approximately A.D. 1260 and 1390. This is also the same time period when records of the shroud begin to appear, suggesting a forgery.
Critics have charged that the researchers who dated the shroud accidentally chose a sample of fabric added to the shroud during repairs in the medieval era, skewing the results. That controversy still rages, but de Wesselow is convinced of the shroud's authenticity from an art history approach.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"It's nothing like any other medieval work of art," de Wesselow said. "There's just nothing like it." [Religious Mysteries: 8 Alleged Relics of Jesus]
Among the anachronisms, de Wesselow said, is the realistic nature of the body outline. No one was painting that realistically in the 14th century, he said. Similarly, the body image is in negative (light areas are dark and vice versa), a style not seen until the advent of photography centuries later, he said.
"From an art historian's point of view, it's completely inexplicable as a work of art of this period," de Wesselow said.
Resurrection: spiritual or physical?
If de Wesselow's belief in the shroud's legitimacy is likely to rub skeptics the wrong way, his mundane explanation of how the image of Jesus came to be is likely to ruffle religious feathers. According to de Wesselow, there's no need to invoke a miracle when simple chemistry could explain the imprint. It's likely, he says, that Jesus' female followers returned to his tomb to finish anointing his body for burial three days after his death. When they lifted the shroud to complete their work, they would have seen the outline of the body and interpreted it as a sign of Jesus' spiritual revival.
From there, de Wesselow suspects, the shroud went on tour around the Holy Land, providing physical proof of the resurrection to Jesus' followers. When the Bible talks about people meeting Jesus post-resurrection, de Wesselow said, what it really means is that they saw the shroud. He cites the early writings of Saint Paul, which focus on a spiritual resurrection, over the gospels of Mark, Matthew, Luke and John, which were written later and invoke physical resurrection.
"The original conception of the resurrection was that Jesus was resurrected in a spiritual body, not in his physical body," de Wesselow said.
These ideas are already receiving pushback, though de Wesselow says he's yet to get responses from people who have read his entire book. Noted skeptic Joe Nickell told MSNBC's Alan Boyle that de Wesselow's ideas were "breathtakingly astonishing," and not in a good way; Nickell has argued on multiple occasions that the shroud's spotty historical record and too-perfect image strongly suggest a counterfeit.
On the other end of the religious spectrum, former high-school teacher and Catholic religious speaker David Roemer believes in Jesus' resurrection, but not the shroud's authenticity. The image is too clear and the markings said to be blood aren't smeared as they would be if the cloth had covered a corpse, Roemer told LiveScience.
"When you get an image this detailed, it means it was done by some kind of a human being," Roemer said.
Unlike many "shroudies," as believers are deprecatingly called, Roemer suspects the shroud was deliberately created by Gnostic sects in the first or second century. A common religious explanation for the markings is that a flash of energy or radiation accompanied Christ's resurrection, "burning" his image onto the cloth. [Top 10 Unexplained Phenomena]
If anything is certain about de Wesselow's hypothesis, it's that it is not likely to settle the shroud controversy. Scientific examinations of the delicate cloth are few and far between — and so are disinterested parties. Roemer, for example, recently arrived at a scheduled talk at a Catholic church in New York only to find the talk had been canceled when the priest learned of Roemer's shroud skepticism. (The Catholic Church has no official position on the shroud's authenticity.)
Meanwhile, de Wesselow said, people who aren't driven by faith to accept the cloth as real generally don't care about the shroud at all.
"The intellectual establishment, if you like, is not interested in shroud science," he said. "It regards it as fringe and it's not interested."
You can follow LiveScience senior writer Stephanie Pappas on Twitter @sipappas. Follow LiveScience for the latest in science news and discoveries on Twitter @livescience and on Facebook.

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.