Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Nuclear fusion technology could get a breakthrough from an unexpected place: mayonnaise.
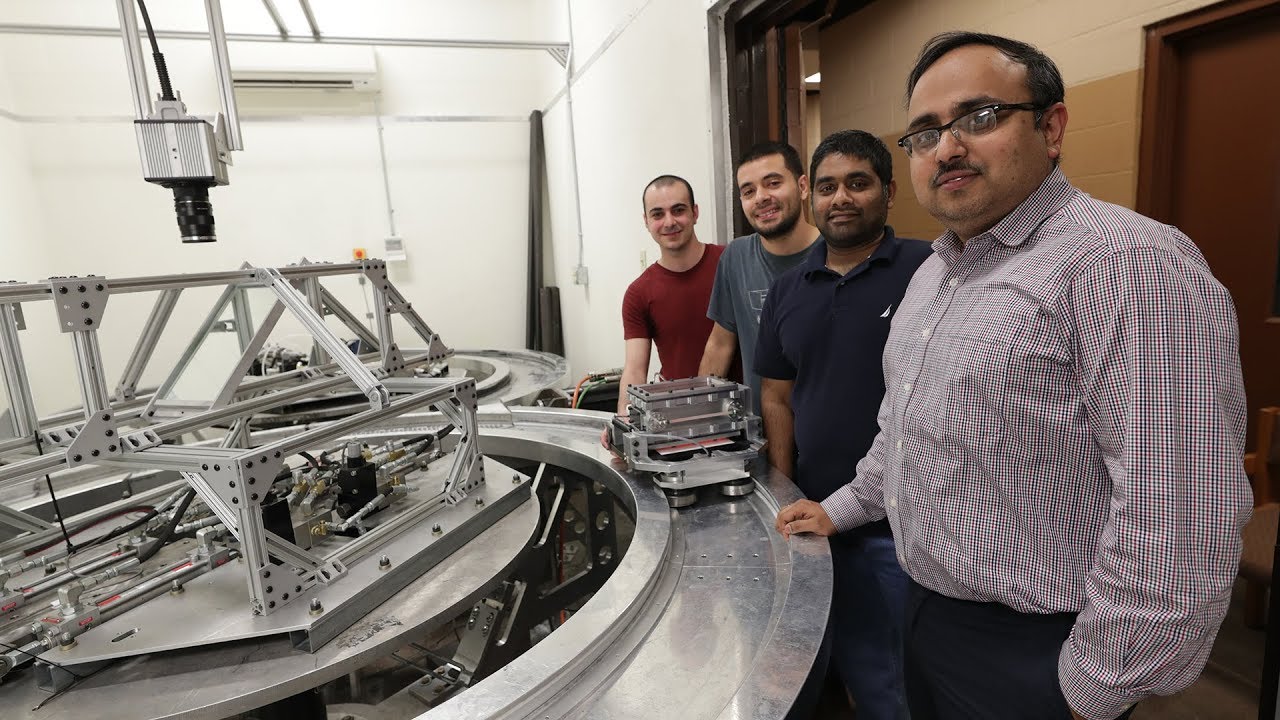
In a new study, published in May in the journal Physical Review E, scientists plopped the creamy condiment into a churning wheel machine and set it whirling to see what conditions made it flow.
"We use mayonnaise because it behaves like a solid, but when subjected to a pressure gradient, it starts to flow," study lead author Arindam Banerjee, a mechanical engineer at Lehigh University in Pennsylvania, said in a statement.
This process could help elucidate the physics that occur at ultrahigh temperatures and pressures inside nuclear fusion reactors — without having to create those extreme conditions.
Related: World's largest nuclear fusion reactor is finally completed. But it won't run for another 15 years.
Nuclear fusion forges helium from hydrogen at the hearts of stars. In theory, it could be the source of nearly limitless clean energy on Earth — if the reaction could produce more energy than it requires to run.
That's a tall order; star-powered fusion occurs at 27 million degrees Fahrenheit (15 million degrees Celsius), according to NASA. And a star's massive gravity forces hydrogen atoms together, overcoming their natural repulsion. On Earth, however, we don't have those crushing pressures, so human-made fusion reactors must run 10 times hotter than the sun.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
To reach these mind-melting temperatures, scientists use multiple approaches, including one called inertial confinement.
In this process, physicists freeze pea-sized pellets of gas — typically a mix of heavy isotopes, or versions, of hydrogen — into metal capsules. Then, they blast the pellets with lasers, which heats the gas to 400 million F (222 million C) in a flash — and, ideally, turns it into a plasma where fusion can occur, according to the statement.
Unfortunately, the hydrogen gas wants to expand, causing the molten metal to explode before hydrogen has time to fuse. This explosion occurs when the metal capsule enters an unstable phase and starts to flow.
Banerjee's team realized that molten metal behaves a lot like mayonnaise at lower temperatures: It can be elastic, meaning it bounces back when you push on it, or plastic, meaning it doesn't bounce back, or flowing.
"If you put a stress on mayonnaise, it will start to deform, but if you remove the stress, it goes back to its original shape," he said. "So there's an elastic phase followed by a stable plastic phase. The next phase is when it starts flowing, and that's where the instability kicks in."
In the new study, the researchers placed mayonnaise in a machine that accelerated the egg-and-oil emulsion until it started to flow. Then, they characterized the conditions at which the condiment transitioned between plastic, elastic and unstable states.
"We found the conditions under which the elastic recovery was possible, and how it could be maximized to delay or completely suppress the instability," Banerjee said.
The study also found which conditions allowed for more energy yield.
Of course, mayonnaise and ultrahot metal capsules are different in many ways. So it remains to be seen whether the team's findings can be translated to a pellet of plasma many times hotter than the sun.

Tia is the editor-in-chief (premium) and was formerly managing editor and senior writer for Live Science. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com, Science News and other outlets. She holds a master's degree in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science writing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia was part of a team at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that published the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won multiple awards, including the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus