153,000-year-old footprints from South Africa are the oldest Homo sapiens tracks on record
A modern dating method has revealed the oldest Homo sapiens' footprints yet, placing bipedal humans in South Africa around 153,000 years ago.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
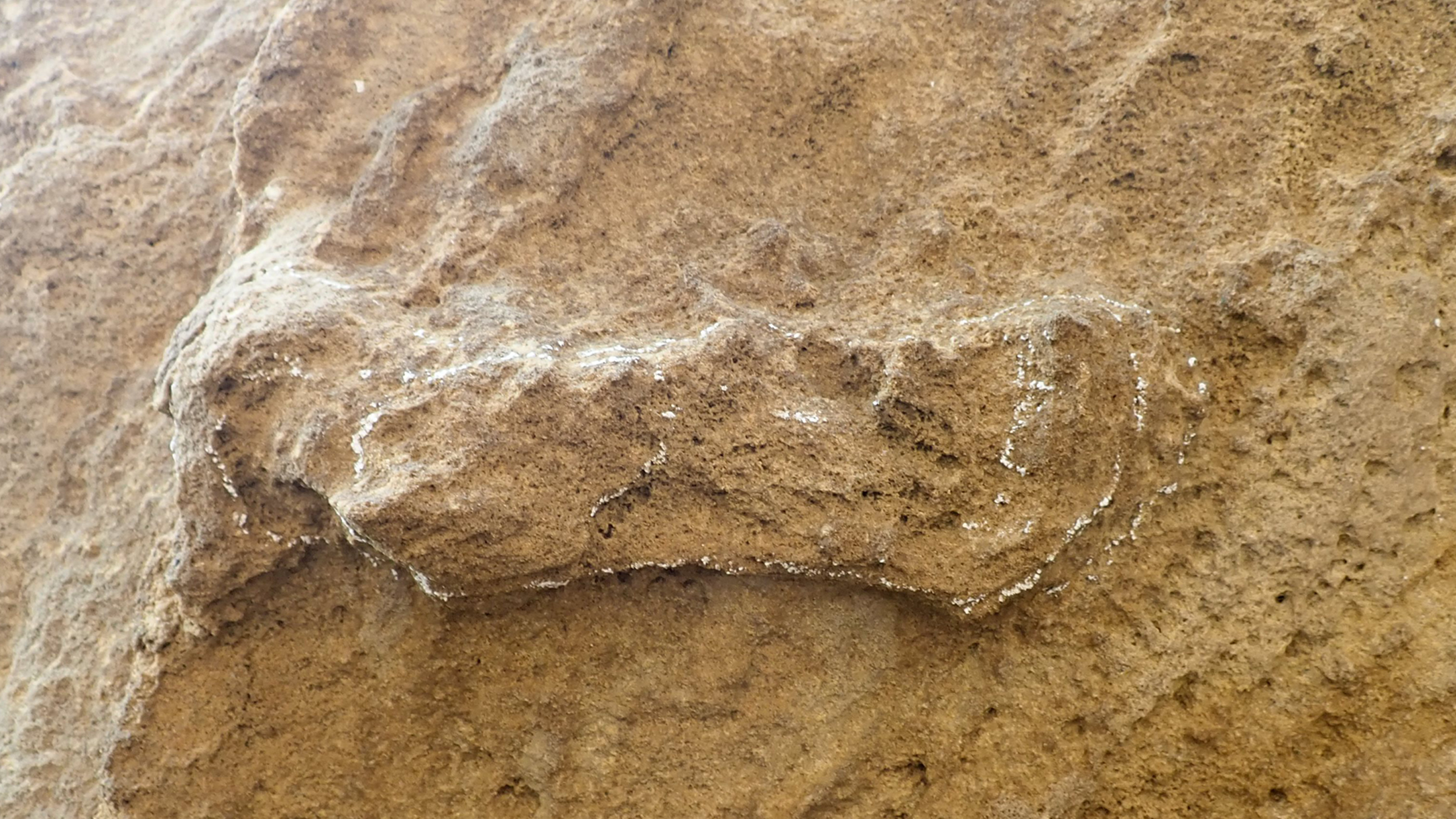
Archaeologists in South Africa have discovered the footprints of Homo sapiens dating to 153,000 years ago, the oldest known tracks attributed to our species, a new study finds.
The record-breaking finding is one of many unearthed in Africa over the past few decades. Since the report of 3.66 million-year-old footprints at the site of Laetoli in Tanzania over 40 years ago, paleoanthropologists have found more than 100 walking trails preserved in rocks, ash and mud left by our hominin ancestors, the group that includes modern and extinct humans as well as our closely-related ancestors.
Seven archaeological sites with tracks left by humans — called “ichnosites” — were discovered just east of the southern tip of the African continent, tens of miles inland from the ancient coast. In an article published April 25 in the journal Ichnos, an international team of researchers used optically-stimulated luminescence (OSL) to figure out when the impressions were made.
Article continues belowThese South African ichnosites included four with hominin tracks, one with knee impressions, and four with “ammoglyphs” — a term denoting any pattern, not just footprints, made by humans that has been preserved over time.
Footprint evidence can add a great deal to the archaeological record, according to the researchers, as it "can provide not just an indication of humans travelling across these surfaces as individuals or groups, but also evidence of some of the activities that they engaged in," the authors wrote in the study. In South Africa, early evidence for modern human behavior includes personal adornment such as jewelry, development of intricate stone tools, the use of abstract symbols, harvesting of shellfish, and coastal cave and rock-shelter sites.
The researchers used OSL to date the South African track sites. This dating method works by estimating the time that has passed since grains of quartz or feldspar in or near the fossilized trackways were last exposed to sunlight. When surfaces that humans walked on were quickly buried, OSL can be used to figure out the date.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Samples from the Garden Route National Park (GRNP) track site, which contains seven identifiable tracks preserved in high cliffs, were dated to 153,000 years ago, plus or minus 10,000 years. Although there are older preserved footprints from other hominin species throughout Africa, Asia and Europe, the GRNP track site is now the oldest one made by Homo sapiens, which evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago.
Most of the samples the team examined dated to between 70,000 and 130,000 years ago, and they were "pleasantly astonished" to find the 153,000-year-old track site, study first author Charles Helm, a research associate at the African Centre for Coastal Palaeoscience at Nelson Mandela University in South Africa, told Live Science in an email.
The discovery has "acted as a spur to continue our search for hominin tracks in deposits we know are even older," Helm said.
The researchers note, however, that attribution of the tracks to a specific species is based more on archaeological artifacts and skeletal remains than on the shape of the tracks themselves. "Not all sites provide conclusive evidence," they wrote in their study, so "controversies and debate are likely to continue."
But the clock is ticking on studying these sites. "We suspect that further hominin ichnosites are waiting to be discovered on the Cape south coast," Helm and study co-author Andrew Carr, a physical geographer at the University of Leicester in the U.K., wrote in The Conversation. "They are also vulnerable to erosion, so we often have to work fast to record and analyze them before they are destroyed by the ocean and the wind."

Kristina Killgrove is a staff writer at Live Science with a focus on archaeology and paleoanthropology news. Her articles have also appeared in venues such as Forbes, Smithsonian, and Mental Floss. Kristina holds a Ph.D. in biological anthropology and an M.A. in classical archaeology from the University of North Carolina, as well as a B.A. in Latin from the University of Virginia, and she was formerly a university professor and researcher. She has received awards from the Society for American Archaeology and the American Anthropological Association for her science writing.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus