Suspected Russian spy whale is looking for love in all the wrong places
A beluga whale that was discovered wearing a suspicious harness in 2019 is on the move in search of other belugas. But it's heading in the wrong direction.
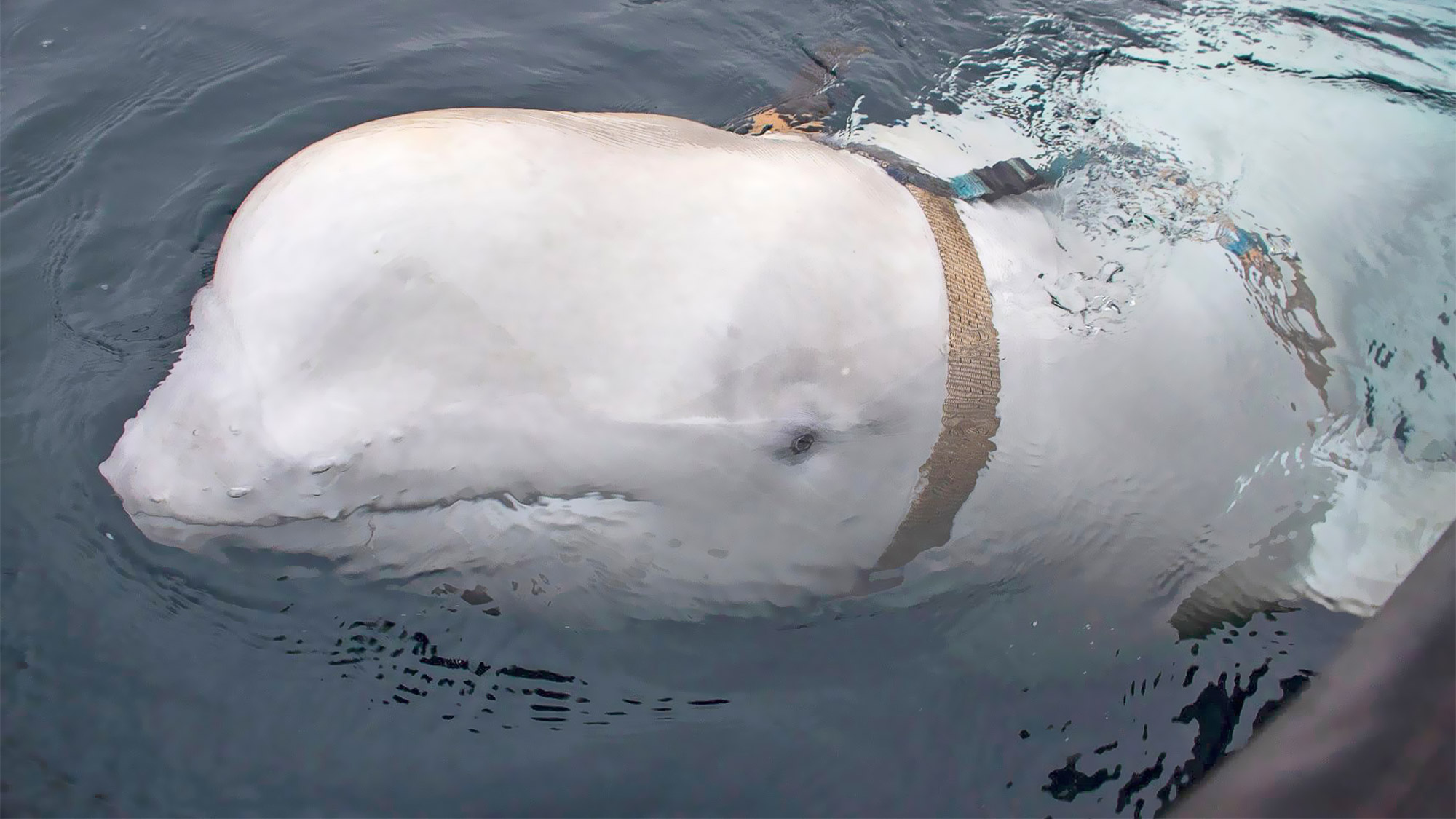
A beluga whale suspected of being an unknowing Russian spy is on the move, possibly in search of love. But it appears that he is headed in completely the wrong direction.
The covert cetacean, known as Hvaldimir, is a male beluga (Delphinapterus leucas) and is believed to be between 13 and 14 years old. Hvaldimir was first spotted in April 2019 in the frigid waters off the coast of Finnmark in northern Norway wearing a harness featuring the words "Equipment of St. Petersburg." The harness was not part of any known beluga whale research project and appeared to have spaces to attach a GoPro camera and other potential spy gear, although nothing was attached at the time. Hvaldimir also displayed no fear of humans, suggesting he had been reared or at least trained by people, which further fueled speculation that he was a spy. Russia has never officially commented on the accusations. (The harness was removed when Hvaldimir was first discovered).
OneWhale, a Norwegian non-profit organization dedicated to protecting Hvaldimir, said that over the last three years, he has spent most of his time in northern Norway. But on May 28, OneWhale spotted Hvladimir near Hunnebostrand, off Sweden's southwestern coast, after rapidly making his way south, French news agency AFP reported.
"We don't know [exactly] why he has sped up so fast," Sebastian Strand, a marine biologist with the OneWhale organization, told AFP. "It could be hormones driving him to find a mate." However, Hvaldimir's current course is taking him "very quickly away from his natural environment," Strand added.
Related: Lone beluga whale spotted 1,500 miles from home, and nobody knows why
Most male belugas reach sexual maturity by the time they are 15 years old, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). So Hvalidimir's hormones could be driving him to search for a mate.
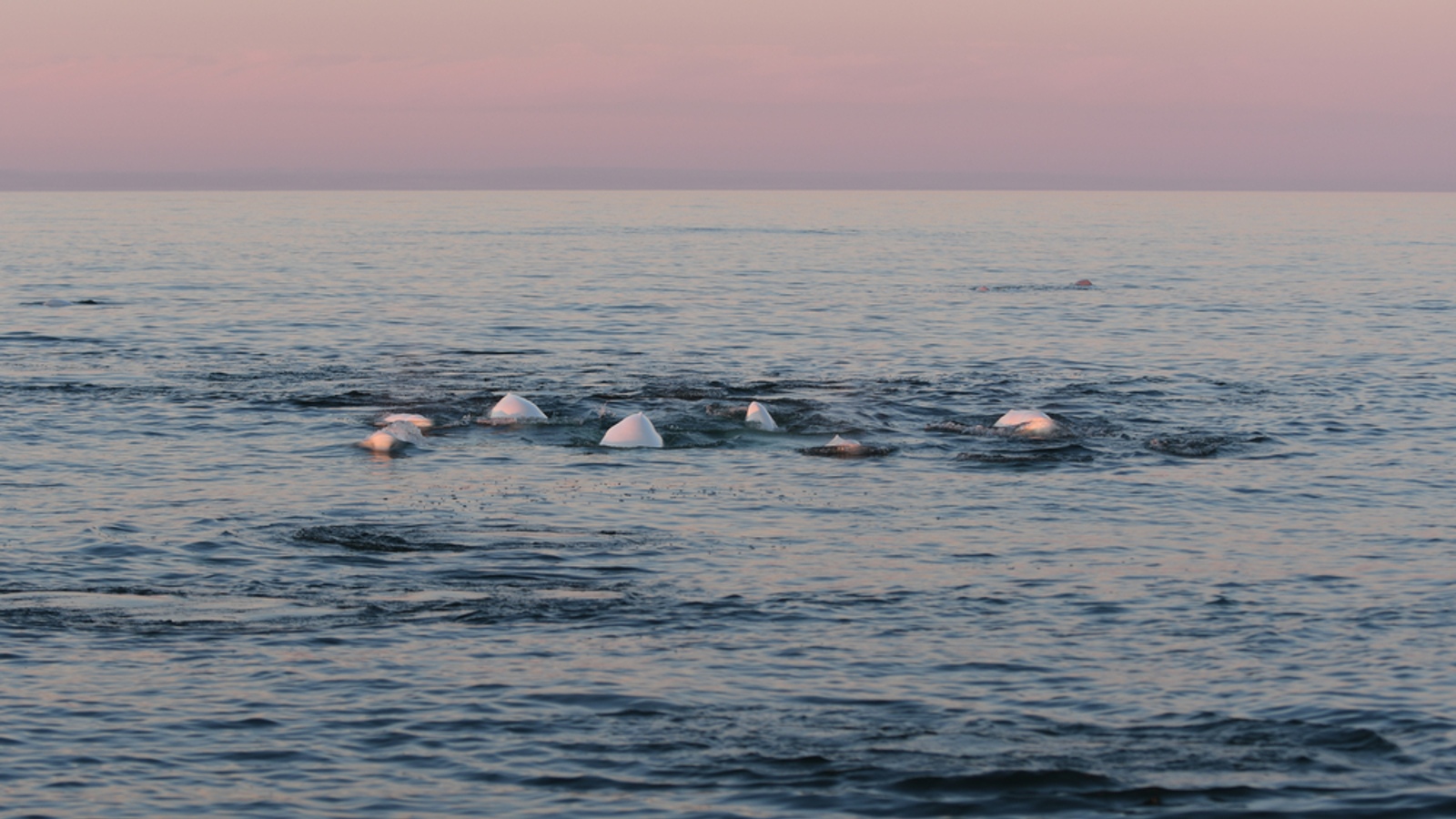
But the lone whale could also just be looking for other belugas regardless of their gender, Strand said. Belugas are very social creatures, and researchers suspect that Hvaldimir has not come into contact with another member of his own species since they began tracking him in 2019.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Regardless of his motivations, Hvaldimir is traveling in the wrong direction. Beluga whales only live in the high Arctic in areas such as Norway's Svalbard archipelago, Greenland, Canada and Russia. There are no known beluga populations in the waters around Sweden.
Experts aren’t sure why Hvaldimir is going in the wrong direction, but it could be that he was released into Norwegian waters from his Russian home as part of his mission, so he has no knowledge of this part of the world. It is also possible that he spent a prolonged amount of time in captivity, which may have dulled his natural instincts, AFP reported.
So far, Hvaldimir seems to be in good health and has been seen hunting wild salmon near fish farms along Norway's border with Sweden. But previous sightings suggest he may have lost some weight, and experts are concerned that he will struggle to find enough food this far south, AFP reported.
OneWhale is now seeking permission from Swedish authorities to catch Hvaldimir and transport him to a fjord in Norway, which can be turned into a refuge for the whale to spend the rest of his days in peace. A pair of captive belugas from China were successfully released into a similar refuge in Iceland in 2020. (Beluga whales frequently live to around 40 years old but can live up to 70 years, according to NOAA).
This is not the first time Russia has been suspected of training cetaceans for military purposes. In April 2022, satellite images suggested the country had trained dolphins to guard one of its Black Sea bases in Crimea. The U.S. Navy has also trained dolphins and sea lions for military operations since 1959, according to the Naval Information Warfare Center.

Harry is a U.K.-based senior staff writer at Live Science. He studied marine biology at the University of Exeter before training to become a journalist. He covers a wide range of topics including space exploration, planetary science, space weather, climate change, animal behavior and paleontology. His recent work on the solar maximum won "best space submission" at the 2024 Aerospace Media Awards and was shortlisted in the "top scoop" category at the NCTJ Awards for Excellence in 2023. He also writes Live Science's weekly Earth from space series.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus