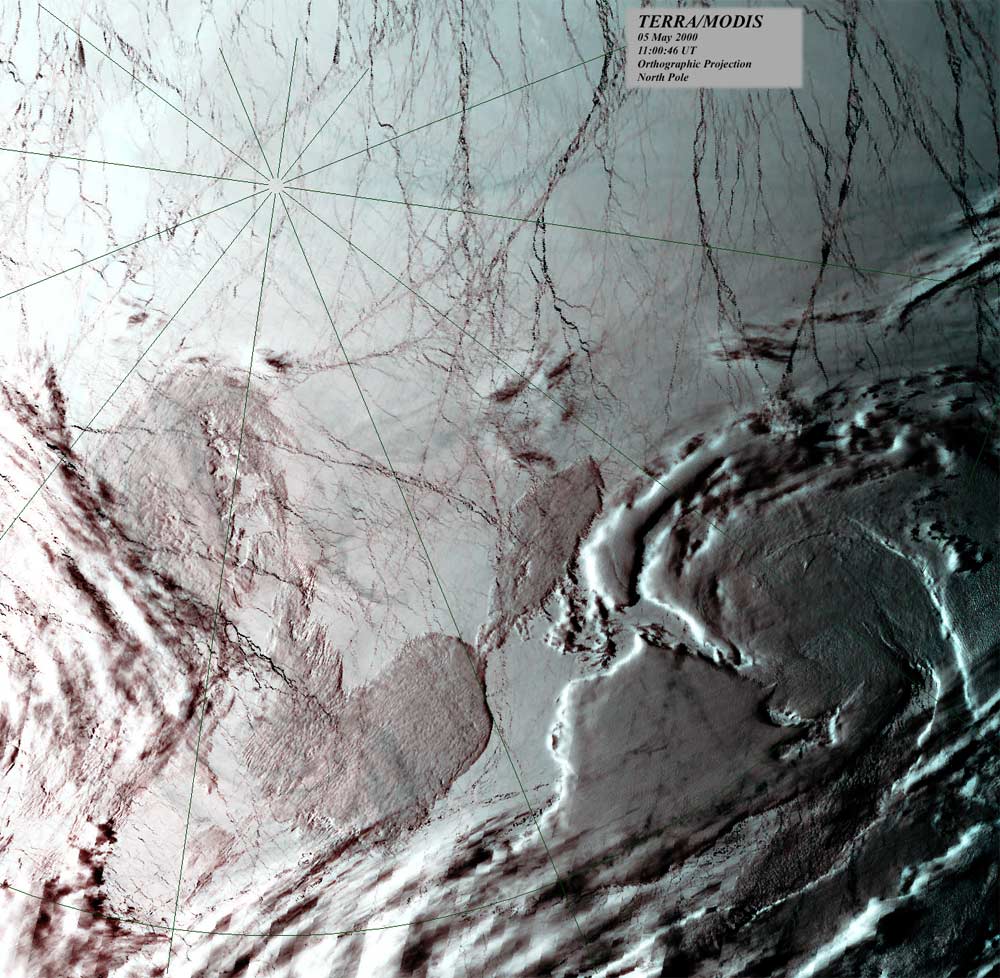
North Pole Moves as Ice Sheets Melt
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
The North Pole’s surprise trip toward Greenland is due to Earth's rapidly melting ice sheets, a new study finds.
The distribution of mass across the planet determines the position of Earth's poles. Because Earth is a bit egg-shaped, the North Pole is always slightly off-center. It's also been slowly drifting south, responding to long-term changes since the last Ice Age, as the enormous ice sheets that once covered large swaths of the planet melted and parts of the Earth rebounded from the lost weight.
But in 2005, the pole suddenly started making a beeline east for Greenland, moving a few centimeters eastward each year. The cause? Rapid melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet, finds a study published May 13 in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. Ice loss and the associated sea-level rise account for more than 90 percent of the polar shift, Nature News reported.
Melting ice moves mass around by adding water to the oceans and lightening the load on ice-covered crust. Although global ice melt plays a role in the pole's shift, Greenland itself is the primary contributor to the eastward movement, the researchers found. "Both of [those factors] are contributing, but now we can say glacial melting in Greenland produces an observable polar motion," said Clark Wilson, a study co-author at the University of Texas, Austin.
The change is small, dwarfed by the pole's broad wandering circles, which are caused by Earth's bulging midriff (the 14-month Chandler wobble) and an annual wobble related to seasonal shifts. However, "if you remove those effects, you'll see a long-term drift," Wilson told LiveScience.
Using data from NASA's GRACE satellite, which measures Earth's gravity field, the researchers tested whether Greenland's ice loss changed the pole position. The data can track how water and ice shift across the planet. "Mass is moving around all the time," Wilson said.
Knowing the precise location of the North Pole has become a critical part of modern life. It's the foundation of GPS, which guides people with mapping apps, as well as military systems and planes.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Email Becky Oskin or follow her @beckyoskin. Follow us @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.com.

 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus