Ancient 'Mega-Clawed' Creature Had Brain Like a Spider's
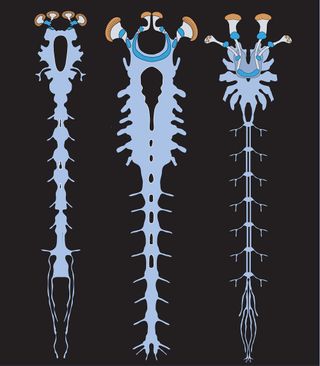
The discovery of a fossilized brain in the preserved remains of an extinct "mega-clawed" creature has revealed an ancient nervous system that is remarkably similar to that of modern-day spiders and scorpions, according to a new study.
The fossilized Alalcomenaeus is a type of arthropod known as a megacheiran (Greek for "large claws") that lived approximately 520 million years ago, during a period known as the Lower Cambrian. The creature was unearthed in the fossil-rich Chengjiang formation in southwest China.
Researchers studied the fossilized brain, the earliest known complete nervous system, and found similarities between the extinct creature's nervous system and the nervous systems of several modern arthropods, which suggest they may be ancestrally related. [Photos of Clawed Arthropod & Other Strange Cambrian Creatures]
The arthropod family
Living arthropods are commonly separated into two major groups: chelicerates, which include spiders, horseshoe crabs and scorpions, and a group that includes insects, crustaceans and millipedes. The new findings shed light on the evolutionary processes that may have given rise to modern arthropods, and also provide clues about where these extinct mega-clawed creatures fit in the tree of life.
"We now know that the megacheirans had central nervous systems very similar to today's horseshoe crabs and scorpions," senior author Nicholas Strausfeld, a professor in the department of neuroscience at the University of Arizona in Tucson, said in a statement. "This means the ancestors of spiders and their kin lived side by side with the ancestors of crustaceans in the Lower Cambrian."

The newly identified creature measures a little over an inch long (3 centimeters), and has a segmented body with about a dozen pairs of attached limbs that enabled it to swim or crawl.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"Up front, it has a long pair of appendages that have scissorlike components — basically an elbow with scissors on the end," Strausfeld told LiveScience. "These are really weird appendages, and there has been a long debate about what they are and what they correspond to in modern animals."
Previously, researchers suggested megacheirans were related to chelicerates, since the extinct creature's scissorlike claws and the fangs of spiders and scorpions have similar structures, said Greg Edgecombe, a researcher at the Natural History Museum in London, England.
"They both have an 'elbow joint' in the same place, and they both have a similar arrangement of a fixed and movable finger at the tip," Edgecombe told LiveScience. "Because of these similarities, one of the main theories for what 'great appendage arthropods' are is that they were related to chelicerates. Thus, our findings from the nervous system gave an injection of new data to support an existing theory."

Fossilized brain images
The researchers used CT scans to make 3D reconstructions of features of the fossilized nervous system. The scientists also used laser-scanning technology to map the distribution of chemical elements, such as iron and copper, in the specimen in order to outline different neural structures.
Though finding a well-preserved ancient nervous system is rare, the new study highlights the potential for similar discoveries, the researchers said.
"Finding ancient preservation of neural tissue allows us to analyze extinct animals using the same tools we use for living animals," Edgecombe said. "It suggests there should be more examples out there."
About a year ago, Edgecombe and his colleagues found a different fossilized brain that revealed unexpected similarity to the brains of modern crustaceans.
"Our new find is exciting because it shows that mandibulates (to which crustaceans belong) and chelicerates were already present as two distinct evolutionary trajectories 520 million years ago, which means their common ancestor must have existed much deeper in time," Strausfeld said in a statement. "We expect to find fossils of animals that have persisted from more ancient times, and I'm hopeful we will one day find the ancestral type of both the mandibulate and chelicerate nervous system ground patterns. They had to come from somewhere. Now the search is on."
The detailed findings of the study were published online today (Oct. 16) in the journal Nature.
Follow Denise Chow on Twitter @denisechow. Follow LiveScience @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience.

Denise Chow was the assistant managing editor at Live Science before moving to NBC News as a science reporter, where she focuses on general science and climate change. Before joining the Live Science team in 2013, she spent two years as a staff writer for Space.com, writing about rocket launches and covering NASA's final three space shuttle missions. A Canadian transplant, Denise has a bachelor's degree from the University of Toronto, and a master's degree in journalism from New York University.
Most Popular


