Rare galaxy with three black holes leads astronomers to the most massive objects in the universe
Scientists watched as a three-quasar system merged in a supercomputer simulation of the universe to birth a black hole 300 billion times as massive as the sun.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
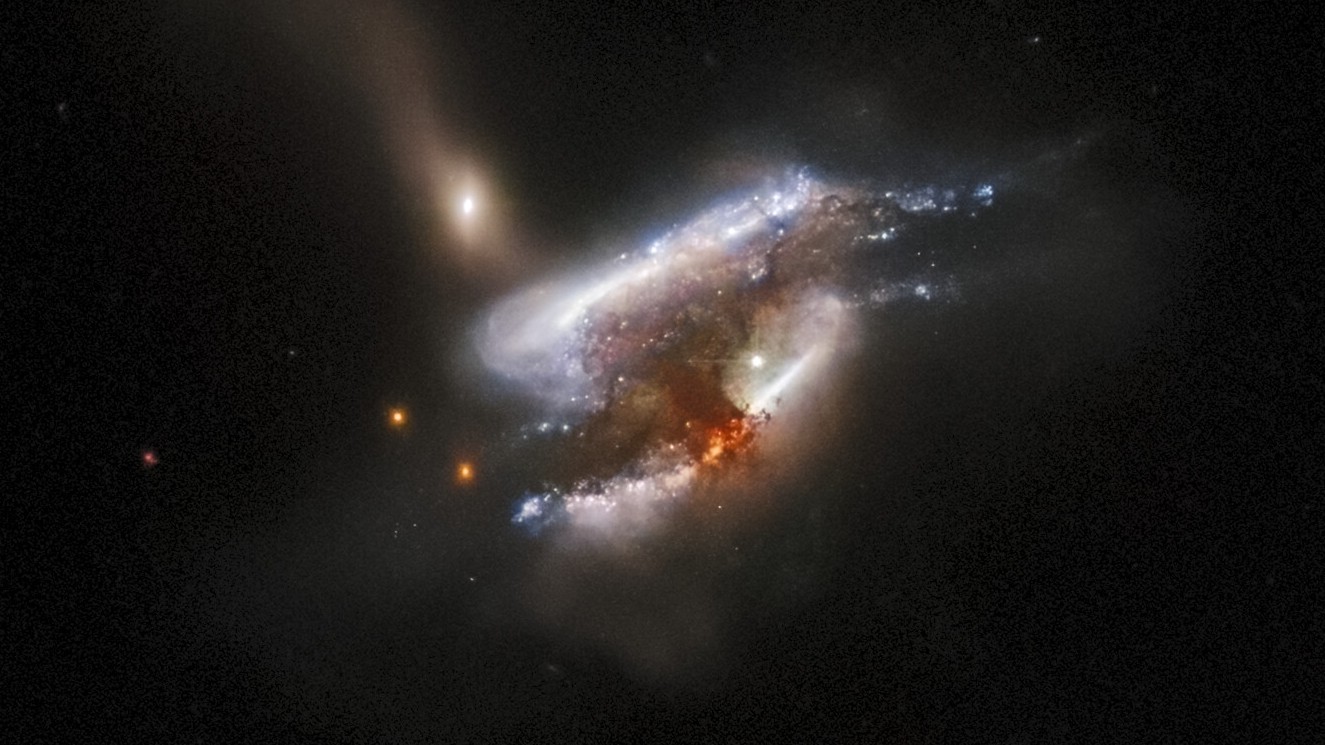
Glimpsed only occasionally at the hearts of massive clusters of galaxies, ultramassive black holes are some of the largest and most elusive objects in the universe. These black hole behemoths have masses exceeding that of 10 billion suns, making them far more monstrous than even the supermassive black holes found at the centers of galaxies like the Milky Way, and their tremendous size has long perplexed astronomers.
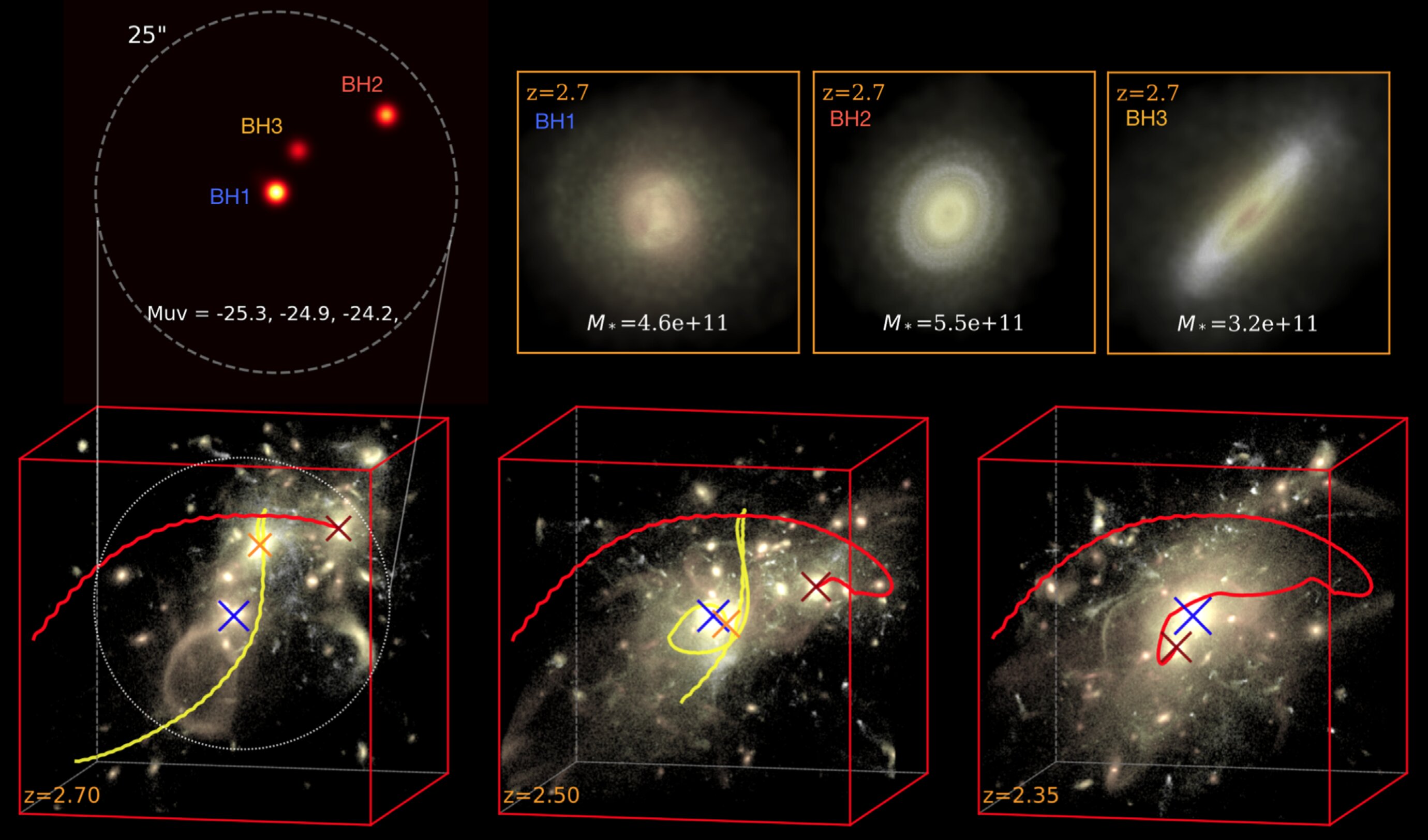
Now, researchers studying a rare galaxy merger with three supermassive black holes at its center may have finally discovered the origins of these cosmic monsters.
Using a high-resolution cosmological simulation called ASTRID, the team modeled the evolution of the universe as it appeared about 11 billion years ago. In the simulation, the team witnessed the birth of an ultramassive black hole following the merger of the three galaxies. Each of these galaxies contained its own quasar, a supermassive black hole that feeds on gas and powers massive outbursts of radiation that can outshine all the stars in their host galaxies combined.
When the triple quasars met, they formed an even more massive black hole while simultaneously triggering a feeding frenzy that allowed the combined object to reach ultramassive status.
"We found a very rare system containing a quasar triplet at the epoch of the cosmic noon — about 11 billion years ago when galaxies and supermassive black holes reach their peak activity," lead study author Yueying Ni, a postdoctoral fellow at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, told Live Science via email. "The system is composed of three bright quasars powered by supermassive black holes, each residing in massive galaxies about 10 times the mass of our galaxy, the Milky Way."
The team's simulation showed the triple quasars likely merged over the course of 150 million years and formed the most massive black hole in the entire simulation, with a mass greater than 300 billion times that of the sun — or more than every star in the Milky Way combined, according to Ni.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
"This indicates a possible formation channel of these ultramassive black holes by extreme merger events of multiple supermassive black holes," Ni said.
The rarity of triple-quasar systems may explain why ultramassive black holes in the actual universe are so elusive.
"Although in general, we expect more massive systems to host more massive black holes, ultramassive black holes are elusive, because black hole growth is a quite self-regulated process," Ni explained. "In an isolated system/galaxy, when a black hole grows massive enough, it will deposit strong feedback to its surroundings and limit itself from further rapid growth."
In other words, astronomers expect that the formation of an ultramassive black hole with a mass even at the lower end of the spectrum (about 10 billion times that of the sun) would happen only in very rare and extreme scenarios. In this case, that comes in the form of repeated mergers of three very massive galaxies.
As follow-up work, the team intends to do a statistical analysis of multiple-quasar systems in the ASTRID simulation to study the properties of their host galaxies, make mock observations, and trace how the ultramassive black hole and the host galaxy evolve as the simulation proceeds.
The research was published Nov. 30, 2022, in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. who specializes in science, space, physics, astronomy, astrophysics, cosmology, quantum mechanics and technology. Rob's articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus