Different Colors Describe Happiness vs. Depression
Are you in a gray mood today? How about a blue funk? Maybe you're seeing red, because you're green with jealousy. The colors we use to describe emotions may be more useful than you think, according to new research.
The study found that people with depression or anxiety were more likely to associate their mood with the color gray, while happier people preferred yellow. The results, which are detailed today in the journal BMC Medical Research Methodology, could help doctors gauge the moods of children and other patients who have trouble communicating verbally.
"This is a way of measuring anxiety and depression which gets away from the use of language," study co-author and gastroenterologist Peter Whorwell of University Hospital South Manchester told LiveScience. "What is very interesting is that this might actually be a better way of capturing the patient's mood than questions."
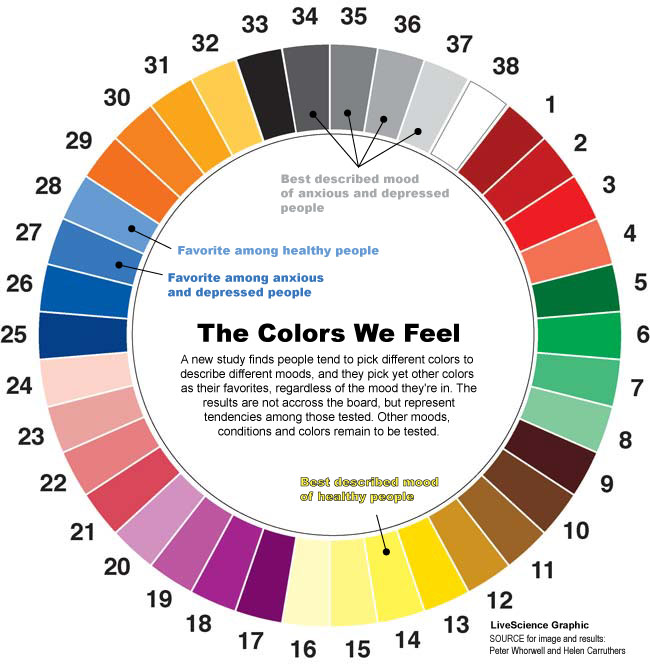
Colors are often used as metaphors for moods, but no one had systematically researched color associations, Whorwell said. To investigate, he and his colleagues picked eight colors — red, orange, green, purple, blue, yellow, pink and brown — and split each into four shades. They then added white, black and four shades of gray for a total of 38 options. After meeting with focus groups, the researchers decided to display the colors in the form of a wheel.
Next, they recruited 105 healthy adults, 110 anxious adults and 108 depressed adults and mailed them printouts of the color wheel. Each person was asked to pick their favorite color, as well as the color they were most "drawn to." Finally, they were asked to pick a color that described their day-to-day mood over the last several months. Another group of 204 healthy volunteers classified each color as positive, negative or neutral.
Whether depressed, anxious or healthy, people liked blue and yellow. Blue 28 on the color wheel was the most popular favorite color among healthy people, while Blue 27 (which is a little darker than 28) got first place among people with anxiety and depression. Meanwhile, Yellow 14 was picked as the color most likely to catch the eye.
But when it came to mood, the groups diverged. Only 39 percent of healthy people associated their mood with a color at all. Of those who did, Yellow 14 was the most popular choice, with about 20 percent of the votes. Meanwhile, about 30 percent of people with anxiety picked a shade of gray, as did more than half of depressed volunteers. In comparison, healthy volunteers described their mood with a shade of gray only about 10 percent of the time.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The researchers also found that when assigning a mood to colors, saturation matters.
"A light blue is not associated with a poor mood, but a dark blue is," Whorwell said. "The shade of color is more important than the color itself."
Whorwell is now testing the wheel on patients with irritable bowel syndrome. He's hoping that color choices can reveal patients' attitudes and predict how well they will respond to treatments like hypnosis. Because people are embarrassed by gastroenterogical symptoms, Whorewell said, non-verbal methods of getting information are sometimes preferable to conversation. And, he said, with additional research, the wheel could be used in medical fields from pediatrics to surgery.
"You've got an instrument now," Whorwell said. "Now people have to play with it and find out the applications."
- What Color Fits Your Mood?
- 7 Thoughts That Are Bad for You
- Top 5 Keys to Happiness

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.


