Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Vibracore machine
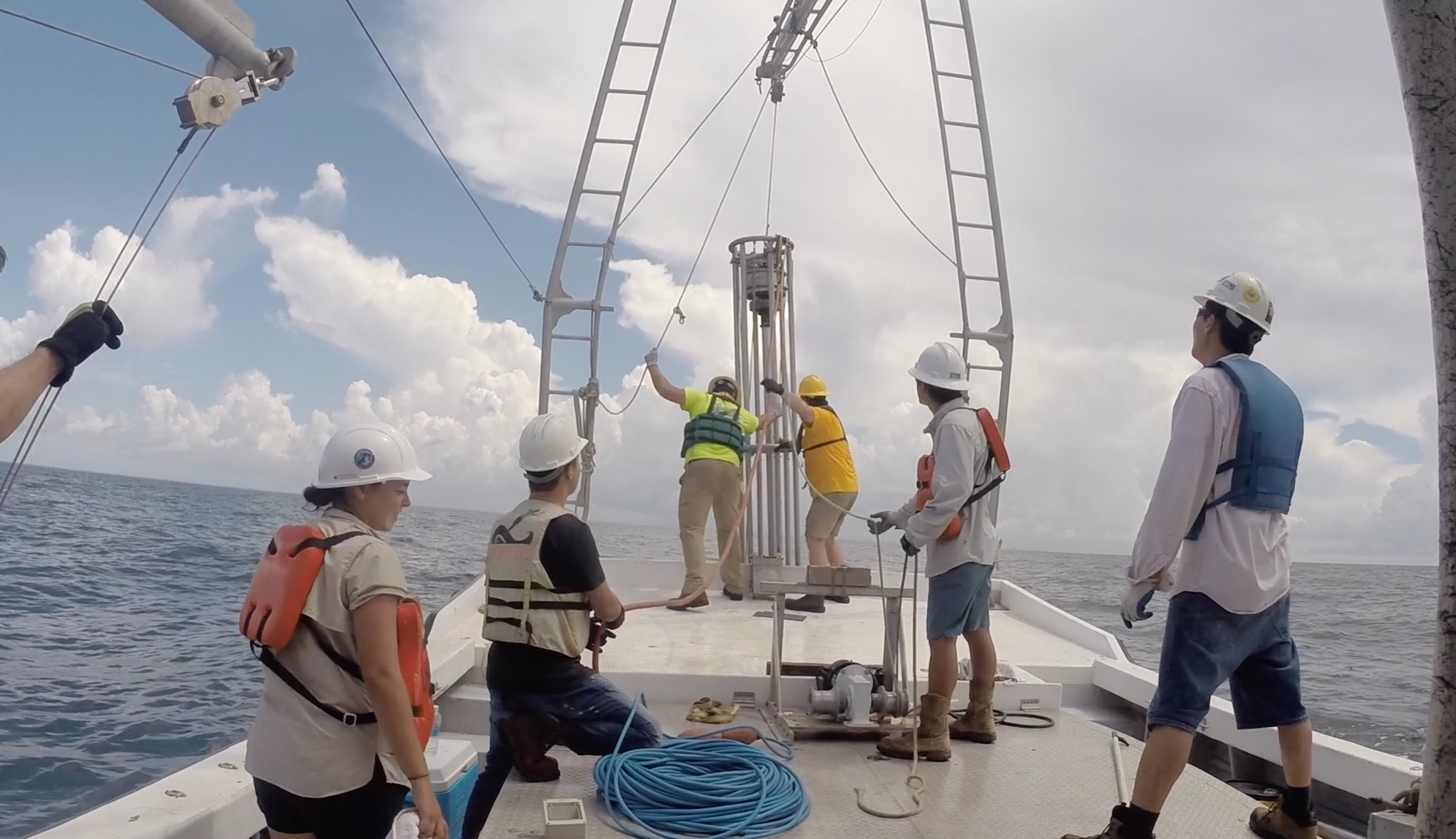

A team from Lousiana State University lower a vibracore machine into the Gulf to capture ancient sediments. The results showed that this forest resembled a North Carolina forest of today, rather than a Gulf Coast forest. In essence, it was a forest designed for a colder climate.
Sediment cores
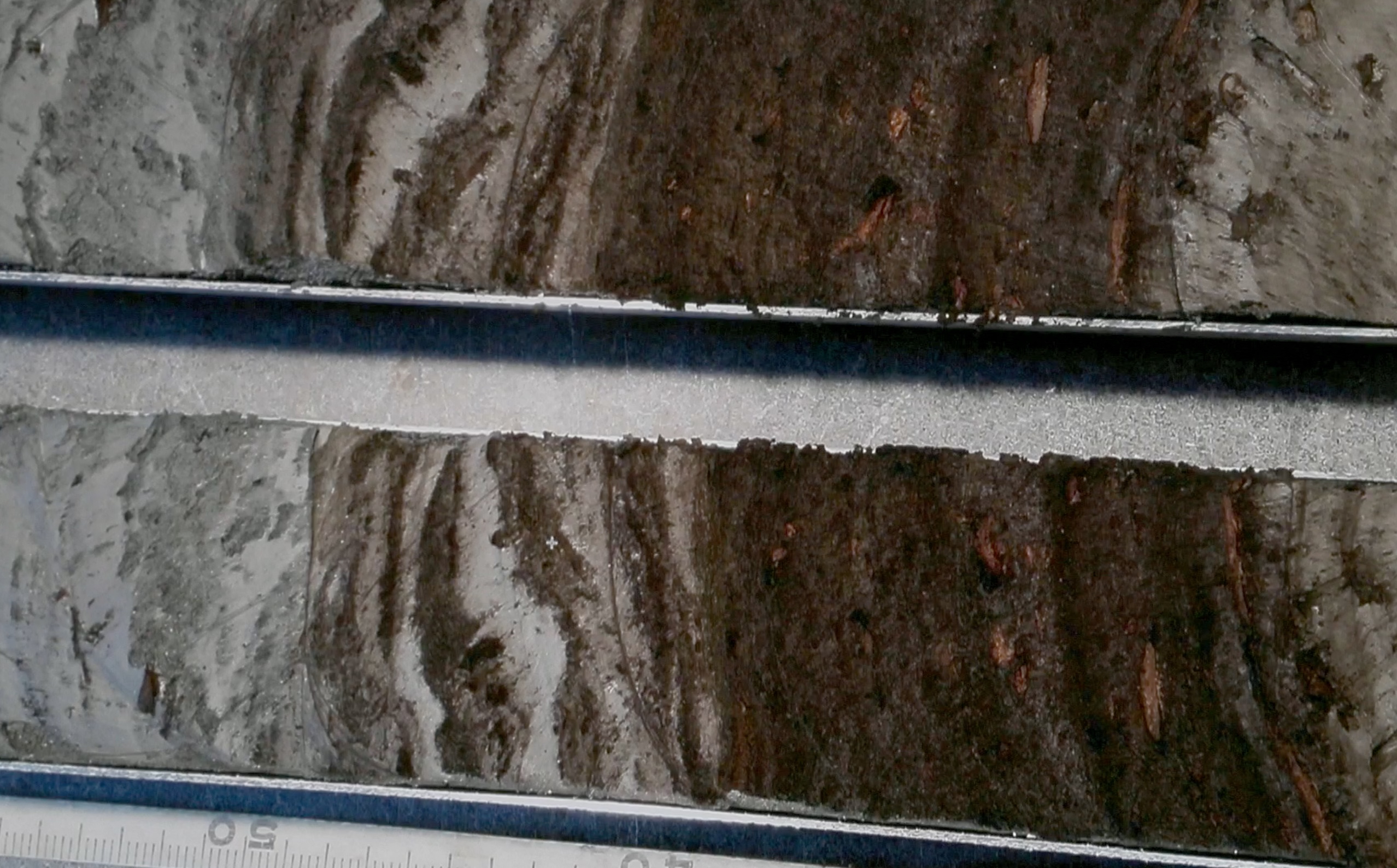

Sediment cores from the Underwater Forest showed that this forest resembled a North Carolina forest of today, rather than a Gulf Coast forest. In essence, it was a forest designed for a colder climate.
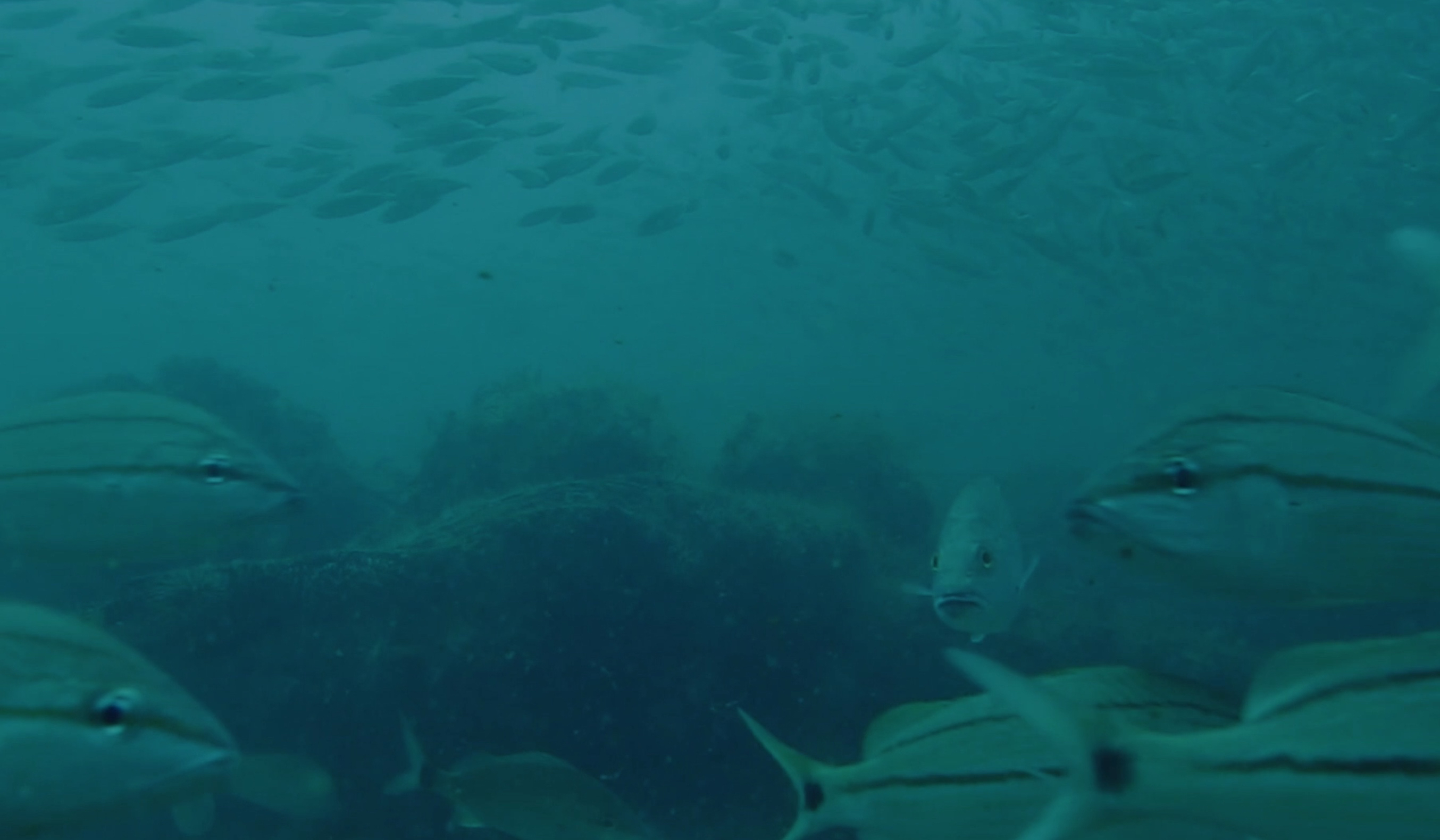
Swimming through
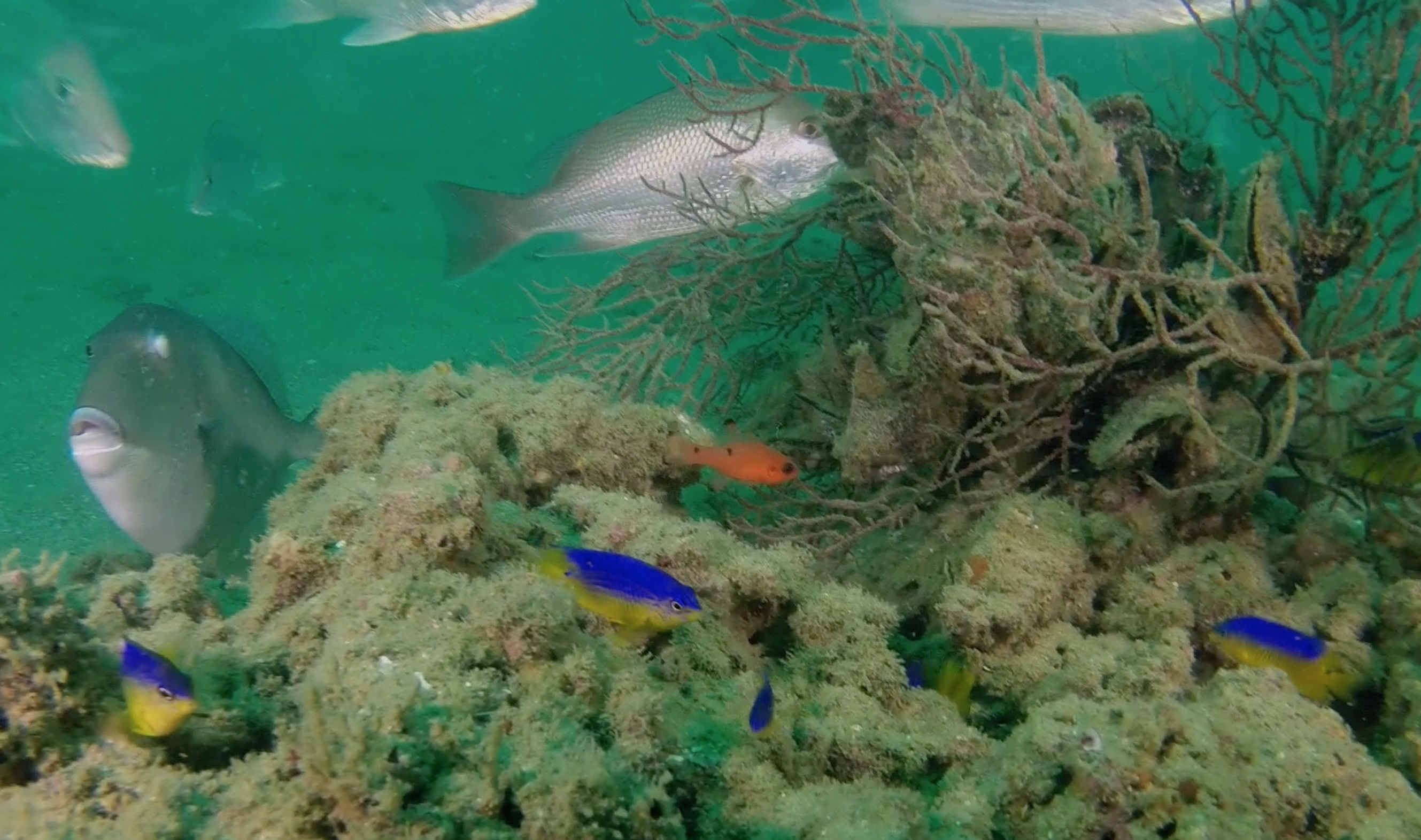

A triggerfish, stage right, eyes a group of juvenile blue and yellow cocoa damselfish. Also known as beau gregories, the small fish transform to a cocoa color when adults.
Knees of the cypress
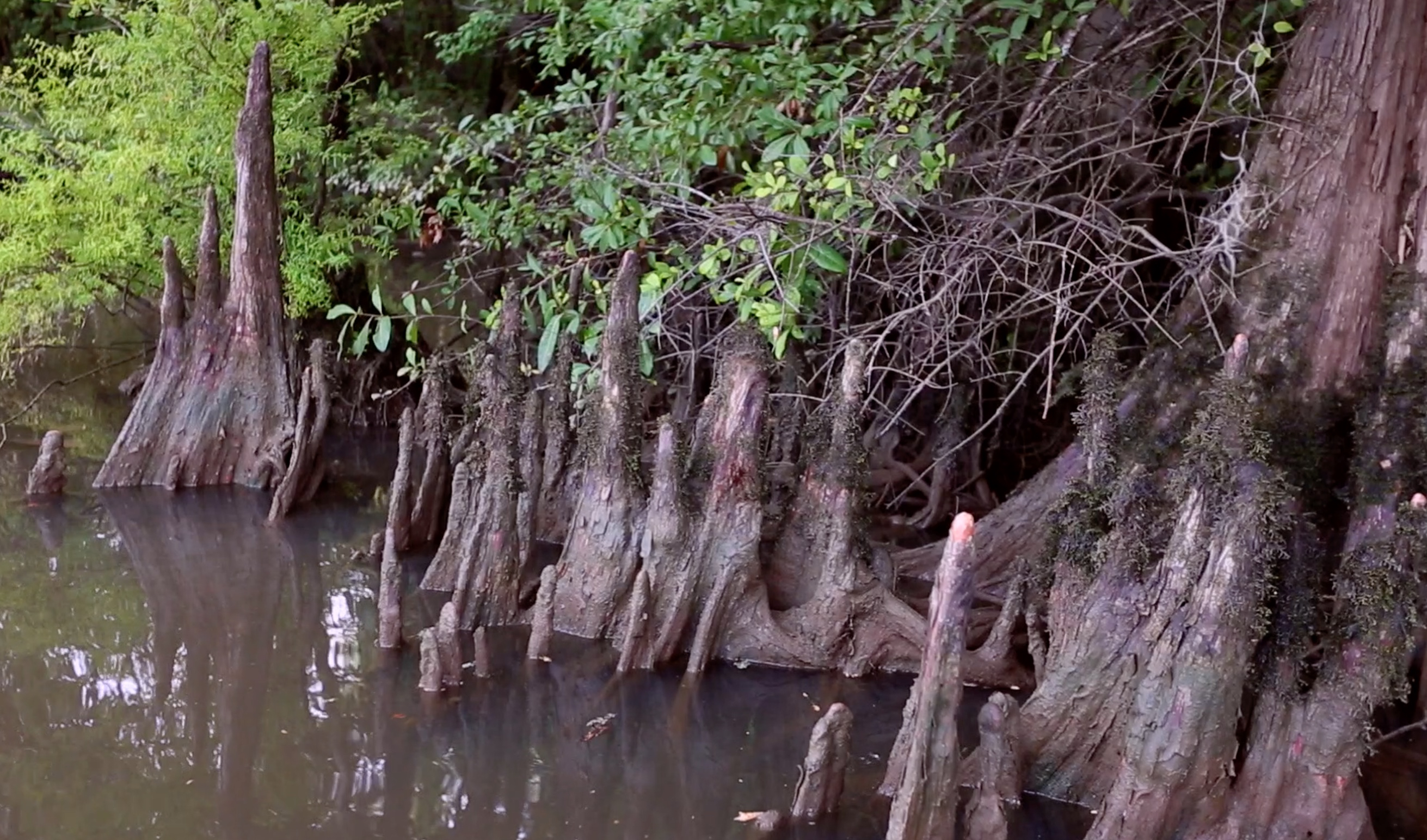

Cypress knees are believed the help the trees stay upright in the soupy mud at the bottom of the great Southern swamps.
Barren landscape
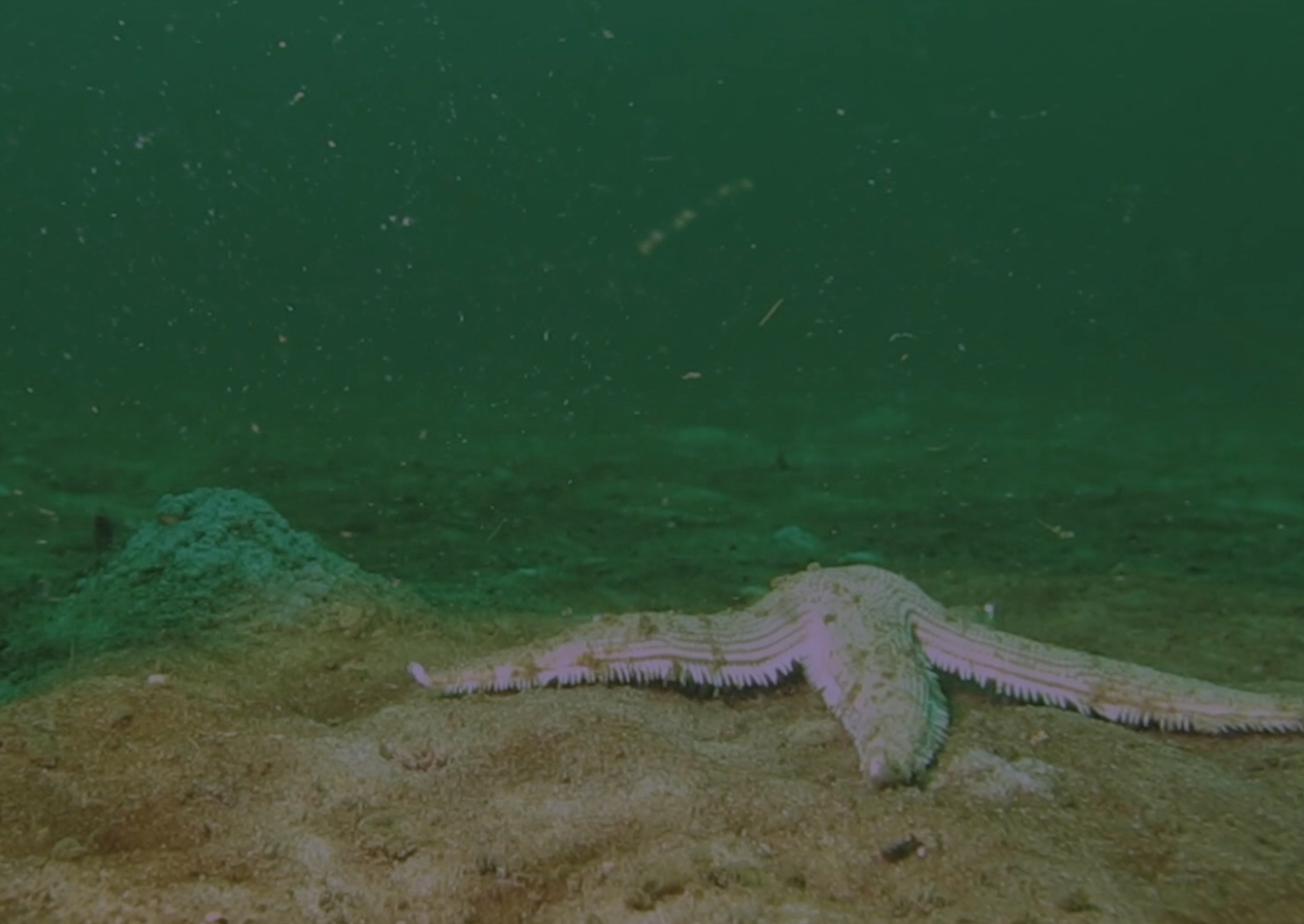

Most of the bottom of the Gulf of Mexico is a barren desert, inhabited by starfish and jellyfish and little else.
Sole sealife
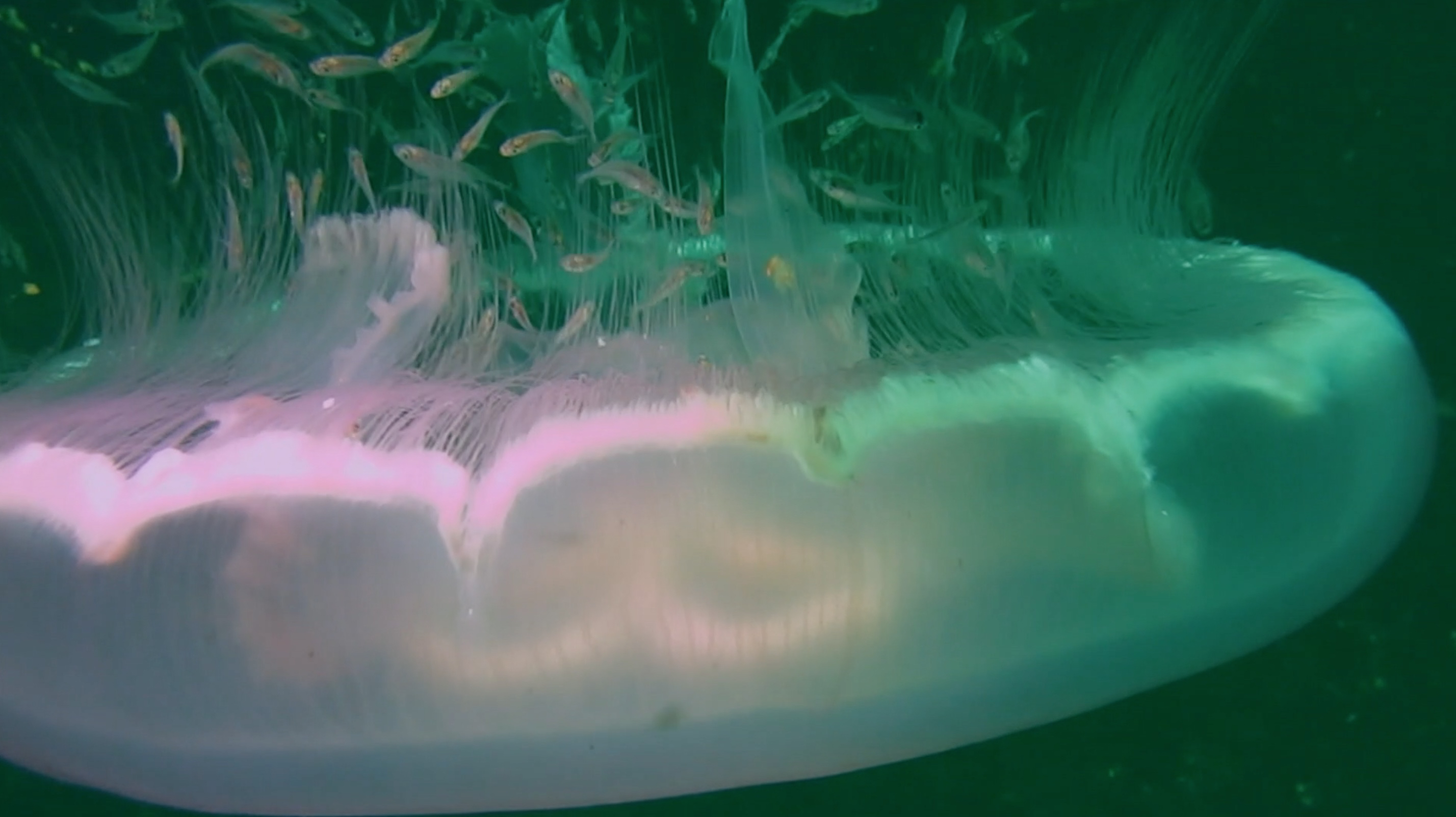
Most of the bottom of the Gulf of Mexico is a barren desert, inhabited by starfish and jellyfish and little else.
Massive stumps

Stumps the size of garbage cans and a log as big around as a telephone pole in this tableau of life on the living reef that the ancient forest has become.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Hurricane Ivan
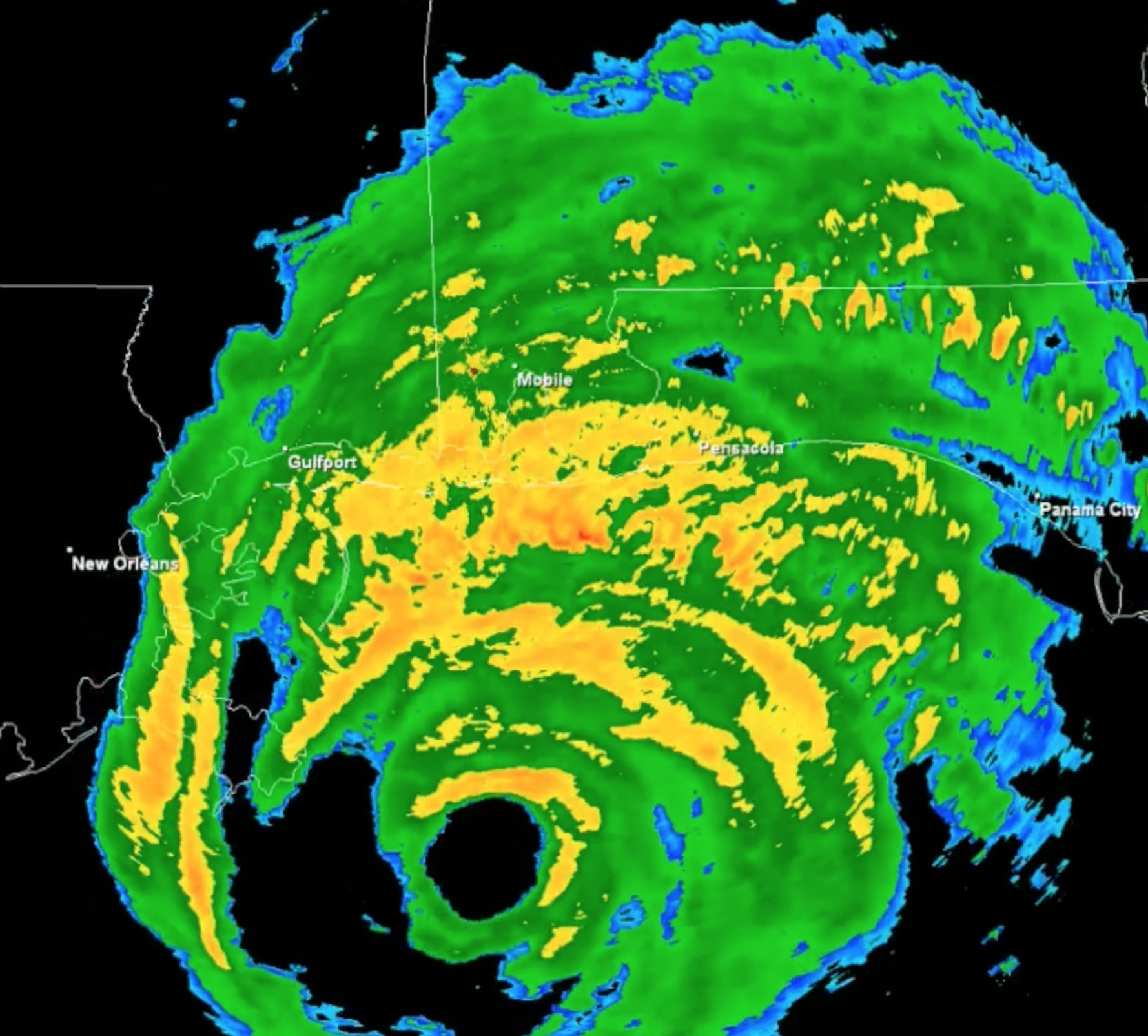

Hurricane Ivan, seen here as it came ashore, passed right over the spot where the Underwater Forest was discovered.

Tia is the editor-in-chief (premium) and was formerly managing editor and senior writer for Live Science. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com, Science News and other outlets. She holds a master's degree in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science writing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia was part of a team at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that published the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won multiple awards, including the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus










