Neolithic women in Europe were tied up and buried alive in ritual sacrifices, study suggests
The research found evidence of the "incaprettamento" method of murder at 14 Neolithic sites in Europe.

The murder of sacrificial victims by "incaprettamento" — tying their neck to their legs bent behind their back, so that they effectively strangled themselves — seems to have been a tradition across much of Neolithic Europe, with a new study identifying more than a dozen such murders over more than 2,000 years.
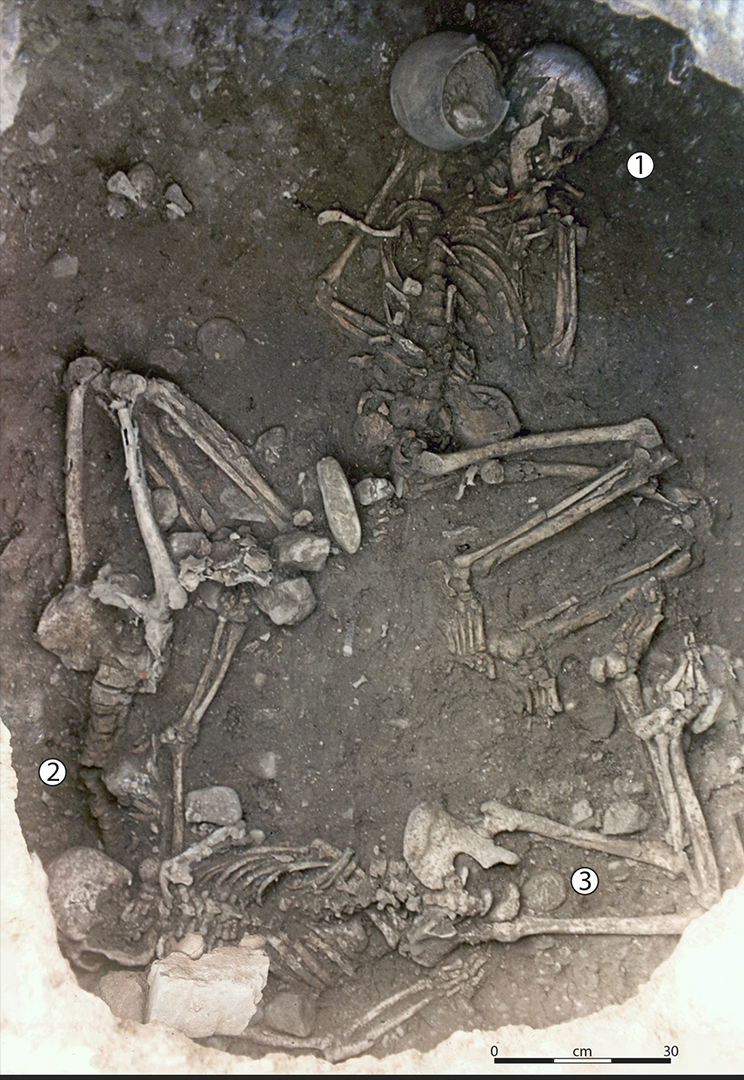
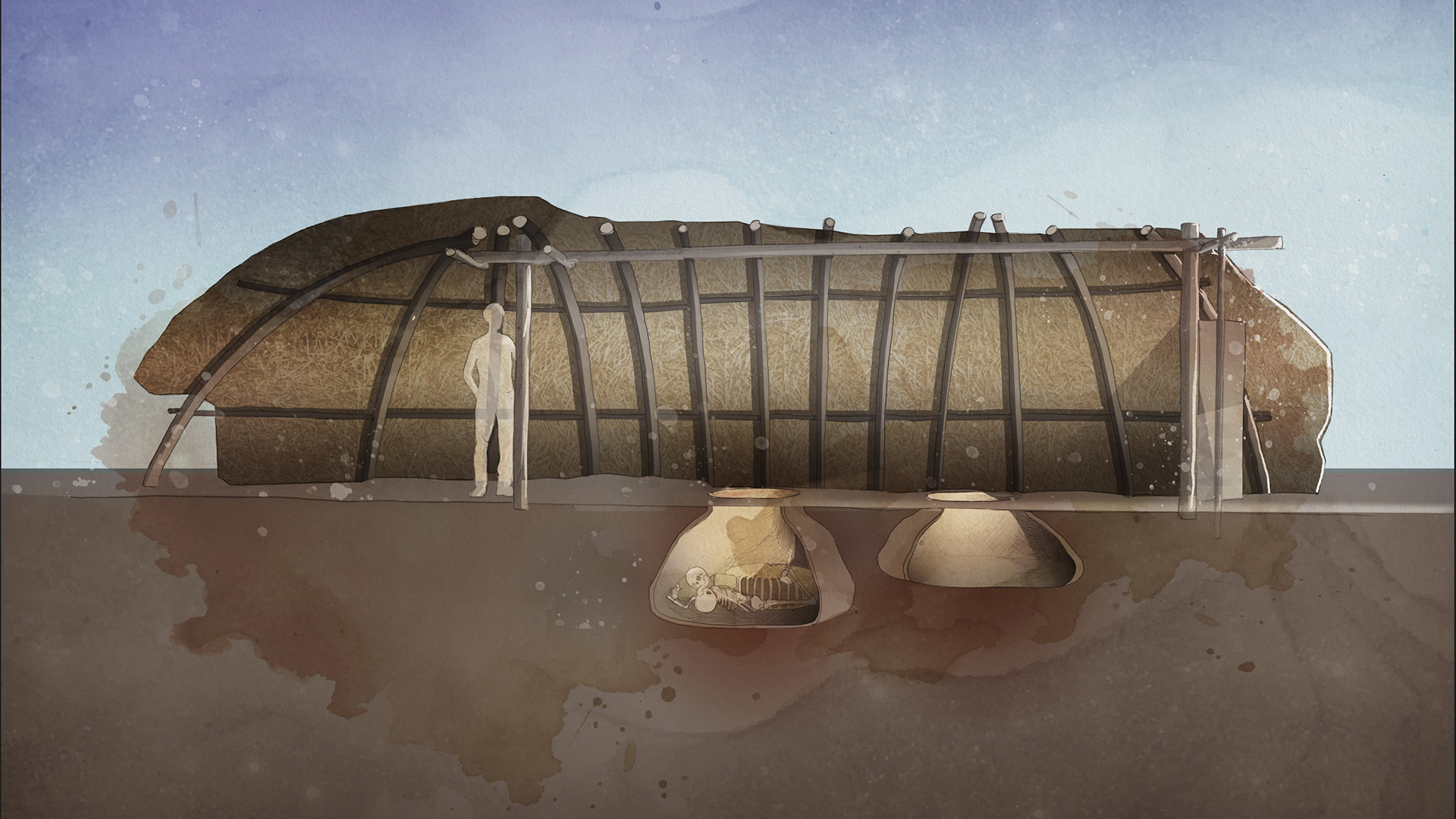
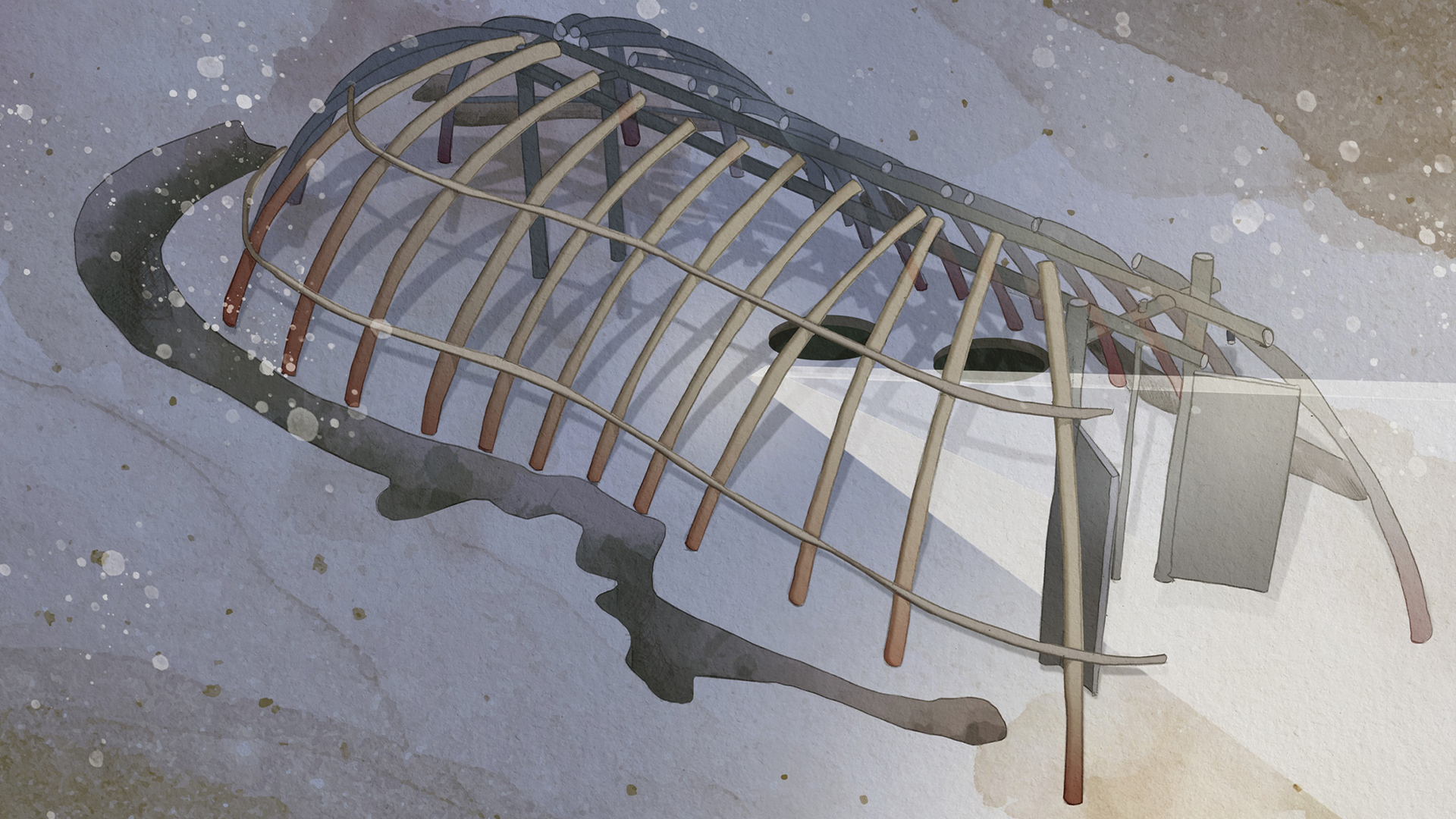
The study comes after a reassessment of an ancient tomb that was discovered more than 20 years ago at Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux near Avignon, in southern France. The tomb mimics a silo, or pit where grain was stored, and it held the remains of three women who were buried there about 5,500 years ago.
The new study, published Wednesday (April 10) in the journal Science Advances, reinterprets the positions of two of the skeletons and suggests the individuals were deliberately killed — first by tying them up in the manner called "incaprettamento" and then by burying them while they were still alive, perhaps for an agricultural ritual.
Study senior author Eric Crubézy, a biological anthropologist at Paul Sabatier University in Toulouse, France, told Live Science that there was a lot of agricultural symbolism to the tomb. He noted that a wooden structure built over it was aligned with the sun at the solstices and that several broken stones for grinding grain were found nearby. "You have the alignment, you have the silo, you have the broken stones — so it seems that it was a rite related to agriculture."
Related: Skull of Neolithic 'bog body' from Denmark was smashed by 8 heavy blows in violent murder
To investigate the idea of human sacrifice at Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux, Crubézy, who worked on the initial discovery of the tomb, and colleagues examined earlier archaeological studies of tomb sites throughout Europe. The team included forensic pathologist Bertrand Ludes, of Paris Cité University and the study's lead author.
They found evidence of 20 probable cases of sacrificial murders using incaprettamento at 14 Neolithic (New Stone Age) sites dating to between 5400 and 3500 B.C. They also found papers describing Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) rock art in the Addaura Cave in Sicily, made between 14000 and 11000 B.C., that seems to depict two human figures bound in the incaprettamento manner.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Crubézy said it appears incaprettamento originated as a sacrificial custom in the Mesolithic period, before agriculture, and later came to be used for human sacrifices associated with agriculture in the Neolithic period.
As a method of human sacrifice, incaprettamento seems to have been widespread across much of Neolithic Europe, with evidence of the practice at sites ranging from the Czech Republic to Spain. The earliest is a tomb near Brno-Bohunice in the Czech Republic that is dated to about 5400 B.C., and the latest is the tomb at Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux, suggesting that the practice persisted for more than 2,000 years, Crubézy said.
Gruesome murders
The bindings used to tie the two individuals at Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux have long since decayed, but a few features of their skeletons — such as the unusual positions of their legs — suggest how they died, Crubézy said.
The third woman in the tomb seems to have been older and likely died from natural causes, the researchers found. She was also interred normally for the time, on her side in the center of the tomb. This suggests that she had been ceremonially buried after her natural death and that the two younger women had been sacrificed to be buried with her, he said.
The two sacrificial victims seem to have been pinned down with heavy fragments of stones used for grinding grain, indicating that, despite their bindings, they were still alive when they were buried, he said.
Today, the gruesome incaprettamento murder method is associated with the Italian Mafia, who have sometimes used it as a form of warning or reprimand.
Crubézy said it wasn't known why incaprettamento was used for Stone Age human sacrifices, but it might have been because a person bound in this way could be seen as strangling themselves, rather than being killed by someone else.
Tom Metcalfe is a freelance journalist and regular Live Science contributor who is based in London in the United Kingdom. Tom writes mainly about science, space, archaeology, the Earth and the oceans. He has also written for the BBC, NBC News, National Geographic, Scientific American, Air & Space, and many others.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus