Siberia's 'gateway to the underworld' is growing a staggering amount each year
The Batagay megaslump — a 3,250-foot-wide (990 meters) depression in the permafrost in the Russian Far East — is "actively growing" by a massive amount every year, scientists have found.
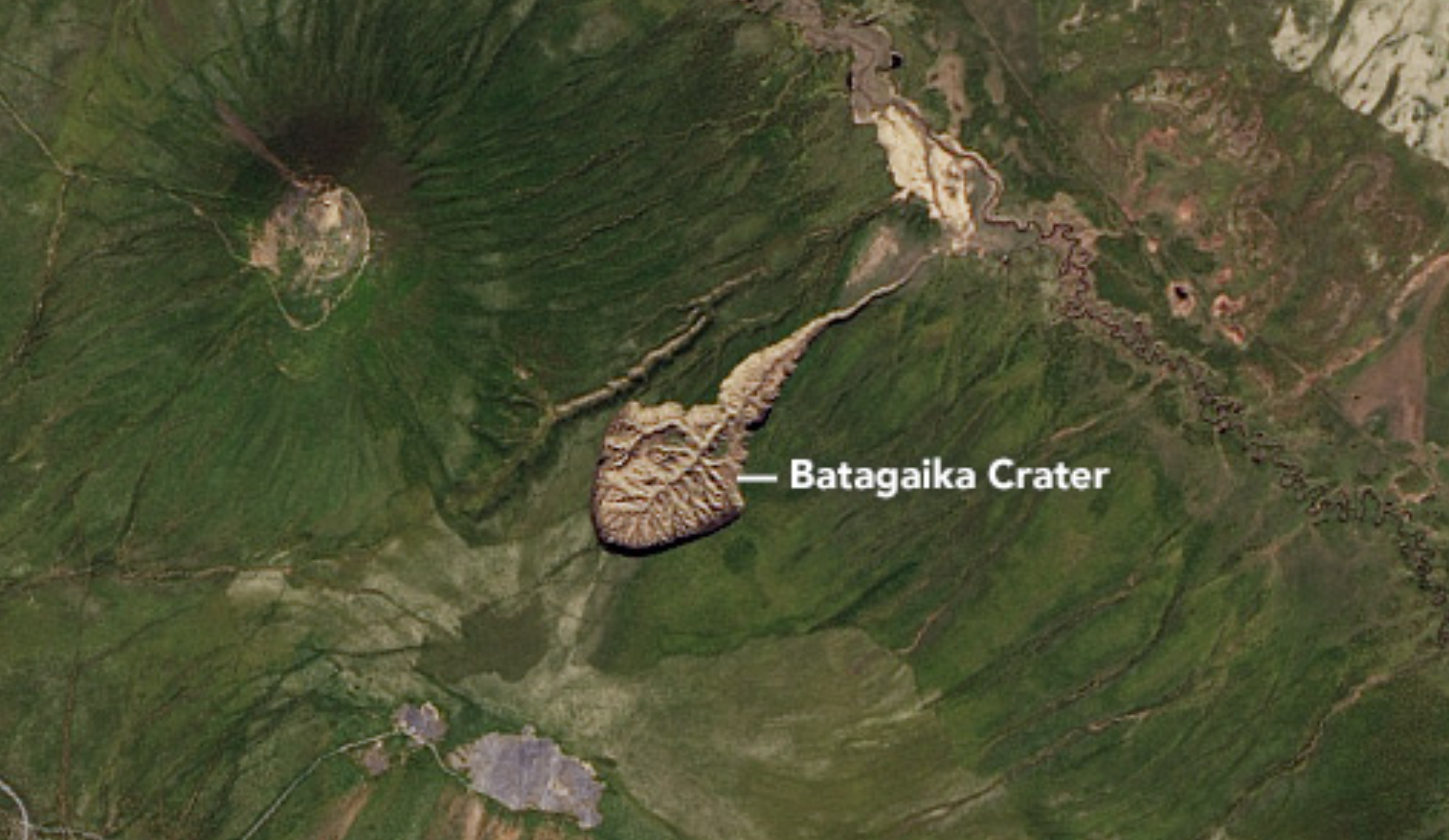
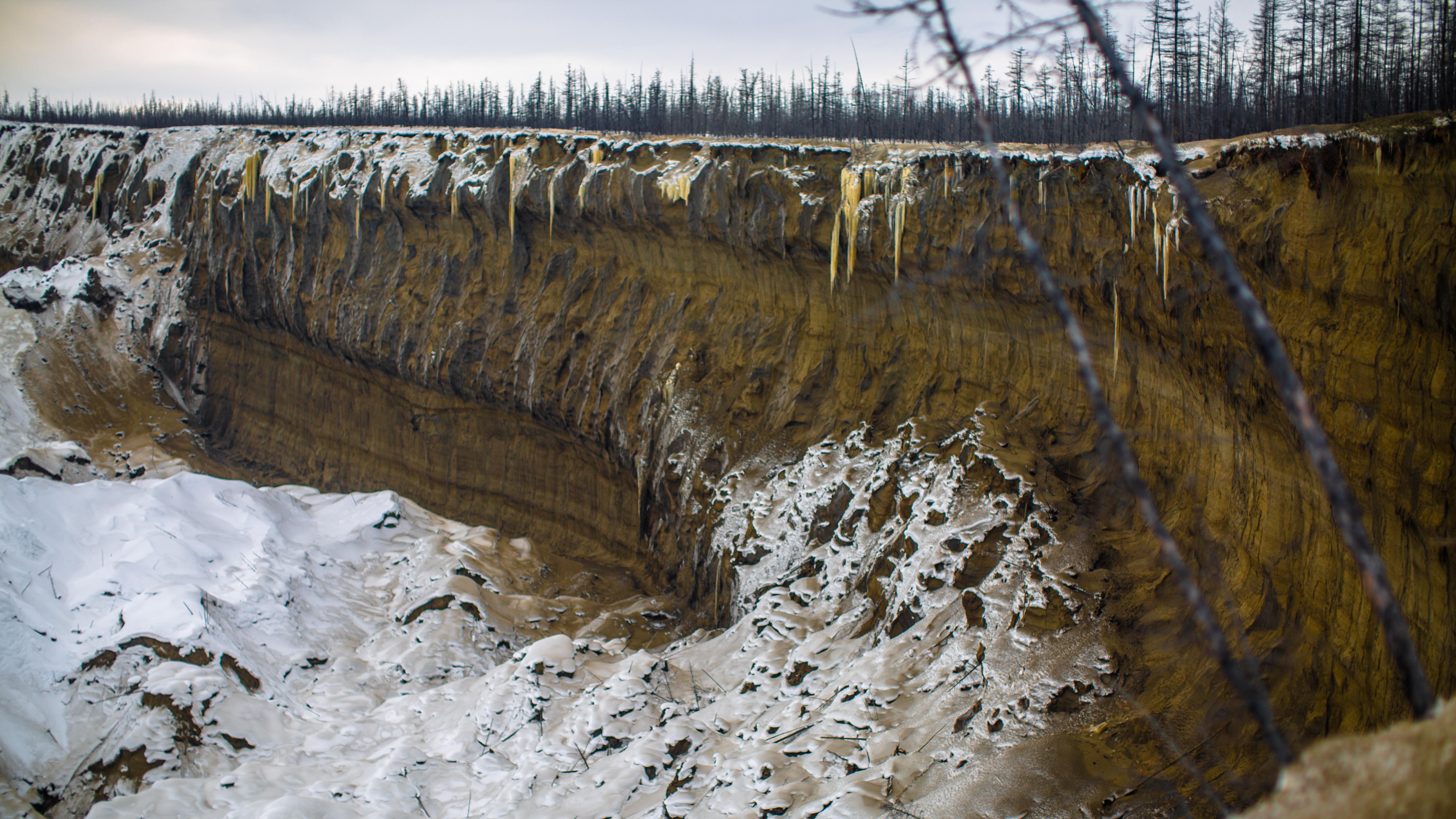
The "gateway to the underworld," a huge crater in Siberia's permafrost, is growing by 35 million cubic feet (1 million cubic meters) every year as the frozen ground melts, according to a new study.
The crater, officially known as the Batagay (also spelled Batagaika) crater or megaslump, features a rounded cliff face that was first spotted on satellite images in 1991 after a section of hillside collapsed in the Yana Uplands of northern Yakutia in Russia. This collapse exposed layers of permafrost within the remaining portion of the hillside that have been frozen for up to 650,000 years — the oldest permafrost in Siberia and second oldest in the world.
New research suggests that the Batagay megaslump's cliff face, or headwall, is retreating at a rate of 40 feet (12 meters) per year due to permafrost thaw. The collapsed section of the hillside, which fell to 180 feet (55 m) below the headwall, is also melting rapidly and sinking as a result.
"Rapid permafrost thaw features are widespread and observed to increase in Arctic and sub-Arctic ice-rich permafrost terrain," the research team wrote in a study, published online March 31 in the journal Geomorphology. However, the amount of ice and sediment lost from the Batagay megaslump is "exceptionally high" due to the sheer size of the depression, which stretched 3,250 feet (990 m) wide as of 2023.
Related: Thawing Arctic permafrost could release radioactive, cancer-causing radon
The megaslump measured 2,600 feet (790 m) wide in 2014, meaning it grew 660 feet (200 m) wider in less than 10 years. Researchers already knew it was growing, but this is the first time they have quantified the volume of melt gushing out of the crater. They did so by inspecting satellite images, field measurements and data from laboratory testing on samples from Batagay.
The results indicated that a region of ice and sediment equivalent to more than 14 Great Pyramids of Giza has melted off the megaslump since it collapsed. The rate of melting has remained relatively steady over the past decade, occurring mostly along the headwall on the western, southern and southeastern edges of the crater.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The Batagay megaslump is "still actively growing," the researchers wrote in the study, but there is a limit to how far it can expand. The permafrost remaining inside the crater is only a few feet thick, so "the possibility of further deepening has practically already been exhausted due to the underlying bedrock geology."

Sascha is a U.K.-based staff writer at Live Science. She holds a bachelor’s degree in biology from the University of Southampton in England and a master’s degree in science communication from Imperial College London. Her work has appeared in The Guardian and the health website Zoe. Besides writing, she enjoys playing tennis, bread-making and browsing second-hand shops for hidden gems.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus






