8,000-year-old rock carvings in Arabia may be world's oldest megastructure blueprints
Around 8,000 years ago, Middle Eastern hunters carved to-scale plans of their 'desert kite' traps onto rocks.

Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Stars and lines engraved in rocks on the Arabian Peninsula may represent nearby hunting traps, making these carvings the first scale-plan diagrams in human history, according to a new study that reveals humans' sophisticated understanding of space around 8,000 years ago.
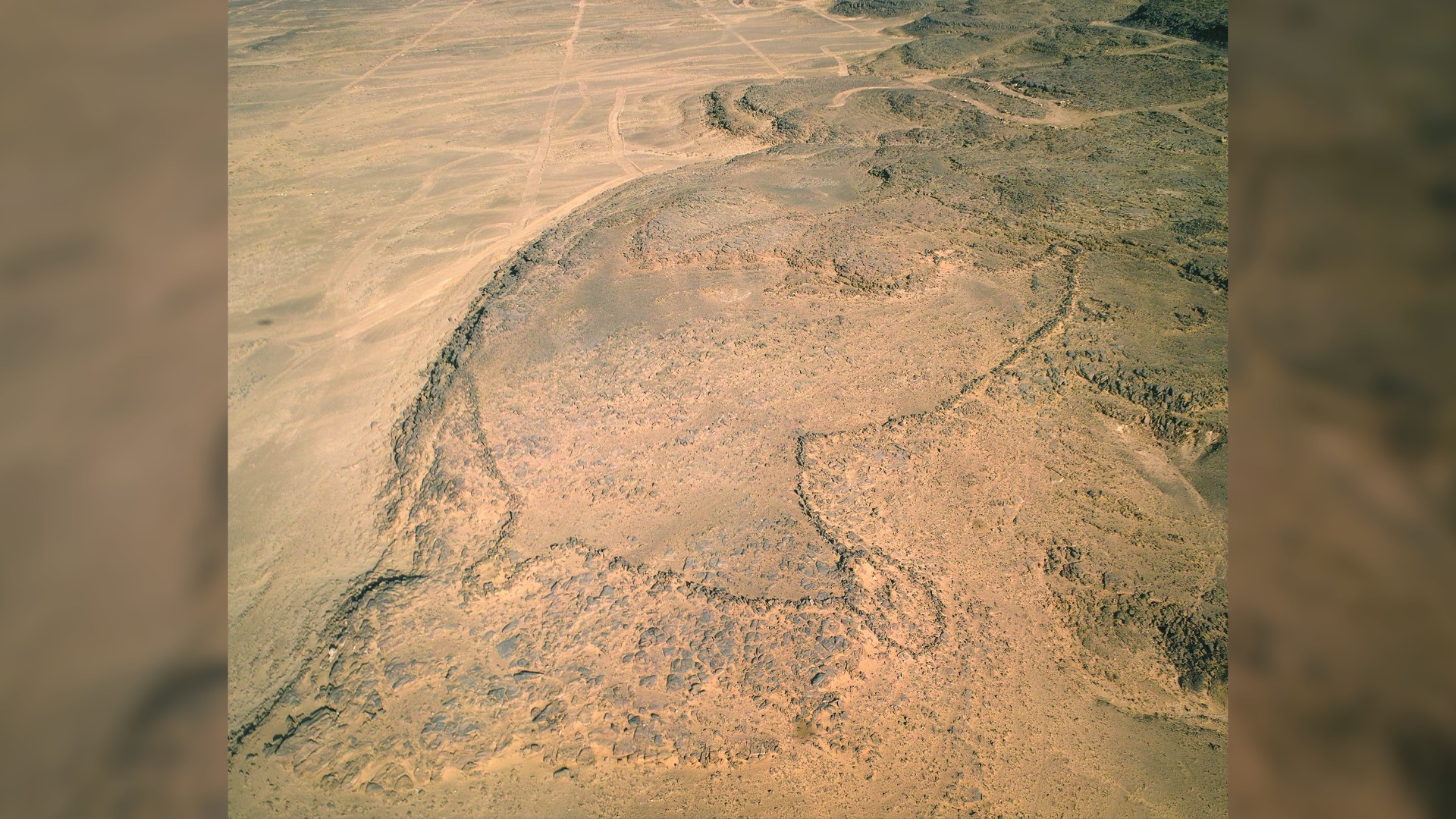
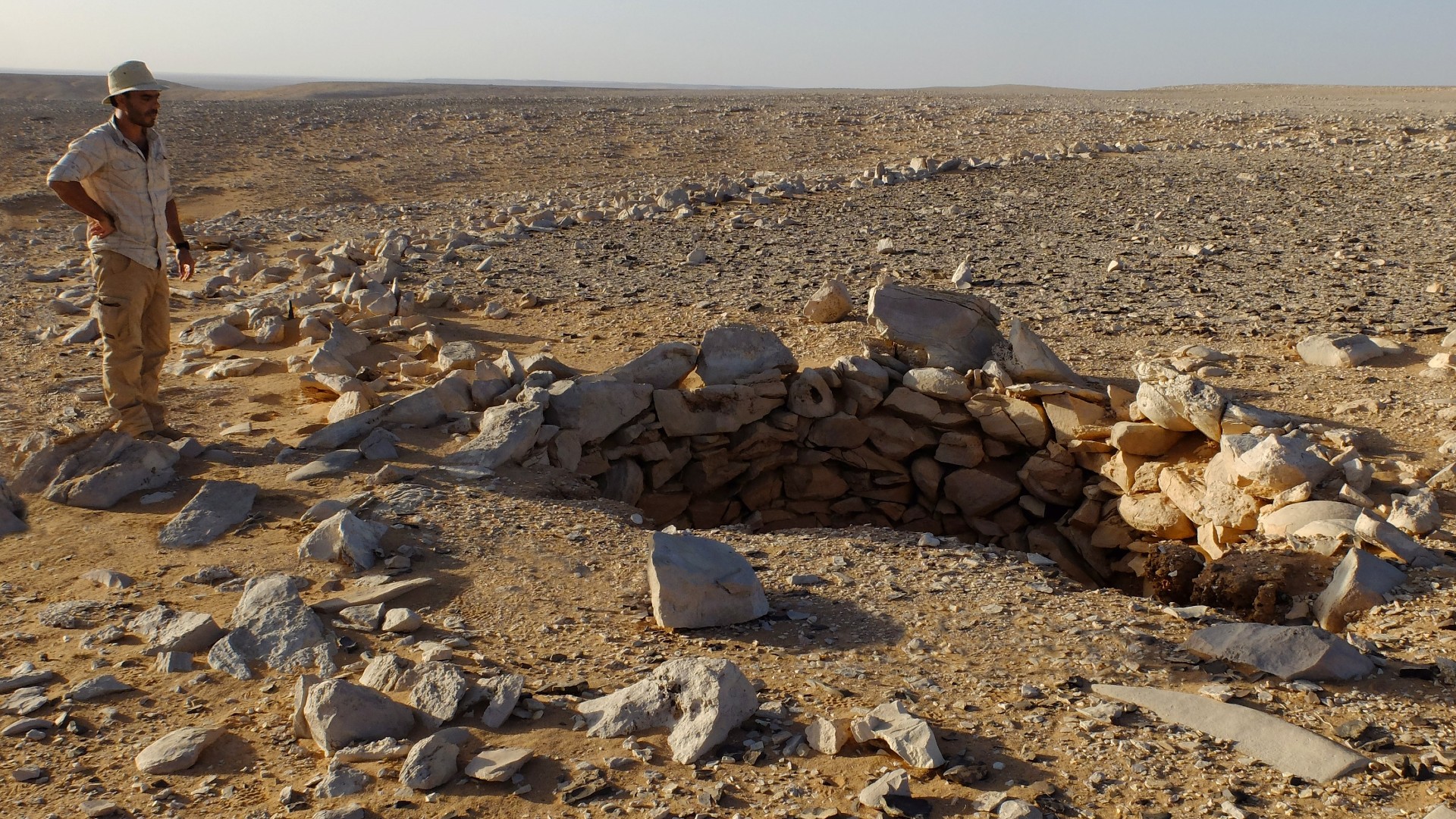
Archaeologists first noticed these structures, known as desert kites, about 100 years ago, when aerial photography began taking off with airplanes. Kites are large areas of land bordered by low stone walls, sometimes with pits scattered on the inside near the edges. Found primarily in the Middle East and Central Asia, kites are thought to have functioned like pens or traps for animals. Hunters would herd animals, like gazelle, into the kite through a long, narrow passage, where the game would be unable to escape the walls or the pits, making them easier to kill.
Because of their massive size — averaging close to the square footage of two football fields — kites cannot be seen in their entirety from the ground. But the advent of publicly available, high-resolution satellite images, such as those from Google Earth, has jump-started the study of desert kites in the past decade.
The recent discovery of architectural-like designs engraved in rocks in Jordan and Saudi Arabia has revealed how Neolithic humans may have planned these "mega-traps," according to a new study, published Wednesday (May 17) in the journal PLOS One.
Related: 7,000-year-old cult site in Saudi Arabia was filled with human remains and animal bones
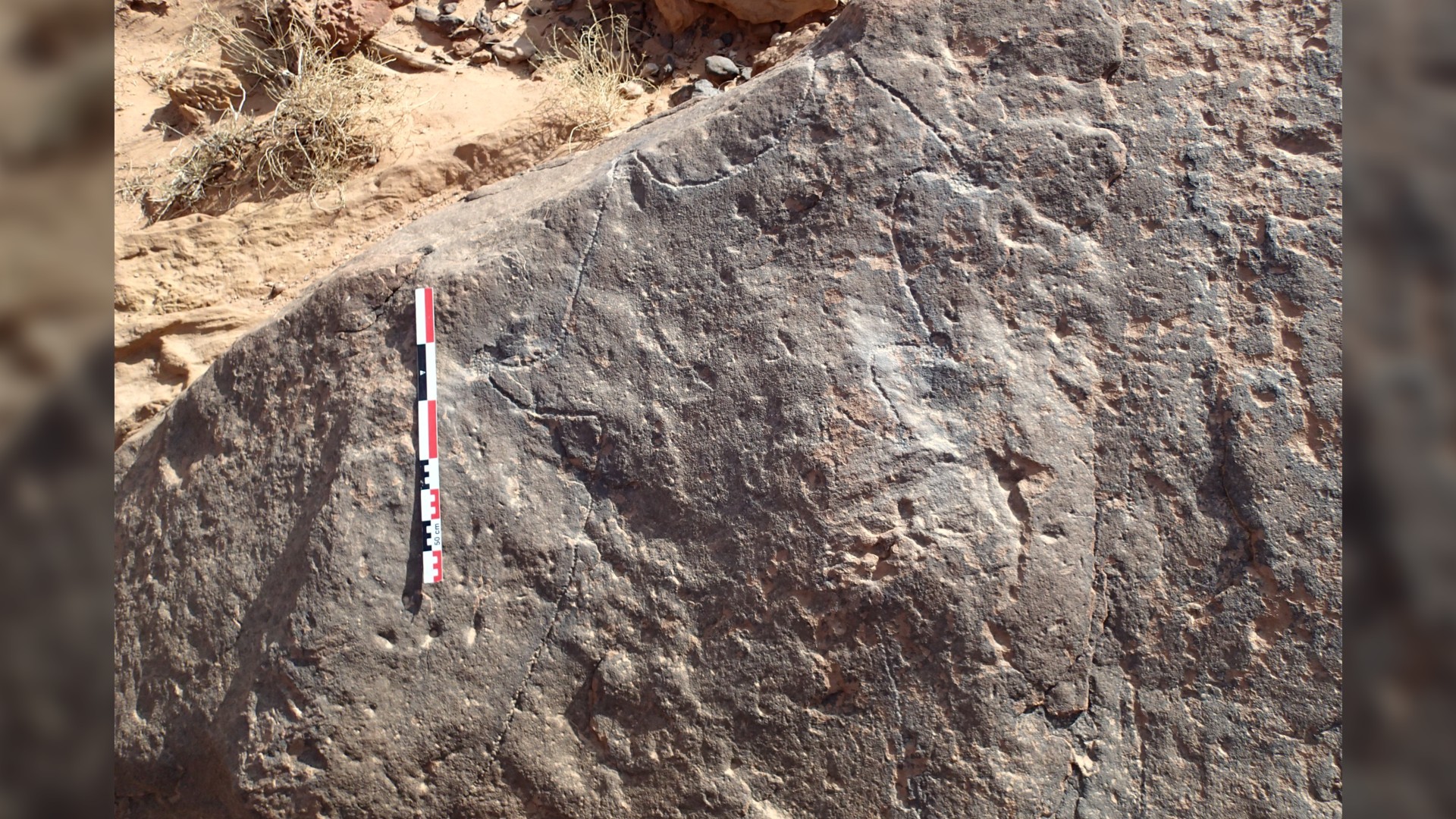
The study authors made mathematical calculations to compare the rock-cut kite diagrams with the shape and dimensions of known kites. Their first example was an engraved limestone monolith from the archaeological site of Jibal al-Khashabiyeh in Jordan. The nearly 3-foot-tall (80 centimeters) stone provided a good canvas for prehistoric people, who carved long, kite-looking lines that drove animals into a star-shaped enclosure, which has eight cup-shaped depressions that represent the pit traps. The stone has different carving techniques, but it's unknown if they represent the work of one person or several people, study first author Rémy Crassard, an archaeologist at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS), told Live Science in an email.
The second example, from Wadi az-Zilliyat in Saudi Arabia, shows two kites carved into an enormous sandstone boulder that's over 12 feet tall and nearly 8 feet across (about 4 by 2 meters). Although made in a different style than the Jordan one, the Saudi Arabia kite diagram also depicts driving lines, a star-shaped enclosure and six cup marks at the ends of the points.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Kites are notoriously difficult to date because they are arrangements of rocks and pits, meaning they don't usually have organic material that's testable with radiocarbon dating. But based on comparisons with neighboring kites associated with sediments and organic remains, the team estimates that these two sites date to about 8,000 years ago, around the end of the Neolithic period in Arabia.
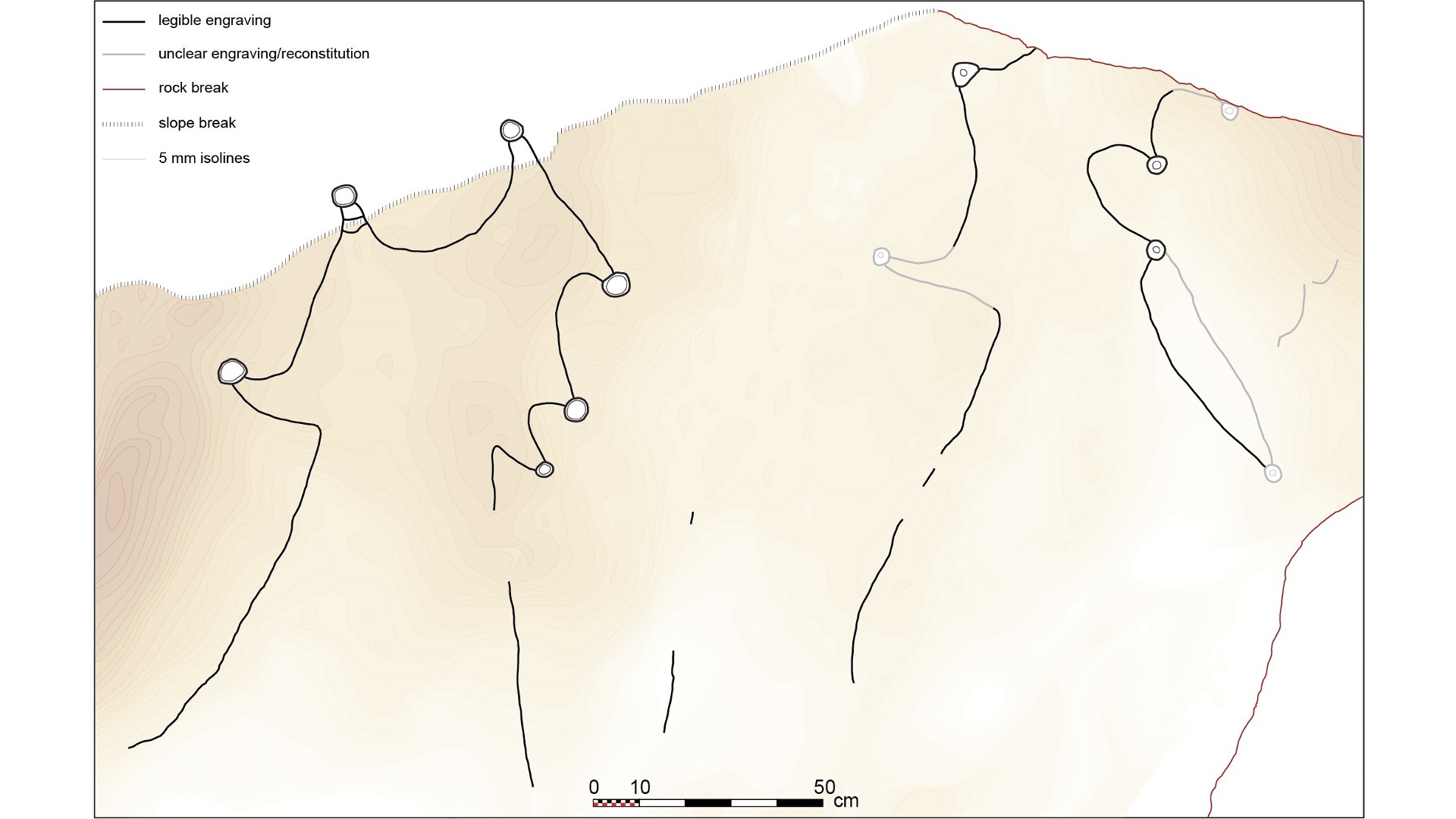

Crassard and colleagues with the Globalkites Project then quantitatively compared the rock-cut diagrams with dozens of plans of known kites through geographical graph modeling. Mathematical comparisons of the engravings with documented kites revealed similarity scores — the diagram from Jordan was found to be most similar to a kite located 1.4 miles (2.3 kilometers) away, while the diagram from Saudi Arabia was most similar to a kite 10 miles (16.3 km) away and very close in appearance to another one 0.87 mile (1.4 km) away.
"The engravings are surprisingly realistic and accurate, and are moreover to scale, as observed by the geometric graph-based assessment of shape similarity," the authors wrote in the study. "These examples of kite representations are thus the oldest known architectural plans to scale in human history."
The team theorized that a group of people preparing for a hunting activity might have studied and discussed the plan of an already-built kite, which might have included coordinating the number and position of the hunters and anticipating the animals' actions ahead of the event. It's also possible that a diagram like this was used to construct the kite in the first place. In either case, the fact that humans were creating a link between physical space as seen from above and graphical representation is an important development in abstract thought and symbolic representation, the researchers suggested in their study.
Jens Notroff, a Neolithic archaeologist at the German Archaeological Institute who was not involved in this research, told Live Science in an email that "the discovery of this specific type of schematic rock art already is an absolutely fascinating addition to our now growing understanding of these Neolithic desert kites and their obviously complex layout within the landscape." Notroff also said "the most stunning insight for me personally is the degree of abstraction — they represent a view none of those participating in construction and use of these desert kites could easily reproduce from their own visual experience."
Crassard and colleagues are continuing their work on desert kites through the Globalkites Project. Although "these engravings are the oldest known evidence of at-scale plans," Crassard said, it is possible that people created similar diagrams in less-permanent material, such as by drawing them in dirt.

Kristina Killgrove is a staff writer at Live Science with a focus on archaeology and paleoanthropology news. Her articles have also appeared in venues such as Forbes, Smithsonian, and Mental Floss. Kristina holds a Ph.D. in biological anthropology and an M.A. in classical archaeology from the University of North Carolina, as well as a B.A. in Latin from the University of Virginia, and she was formerly a university professor and researcher. She has received awards from the Society for American Archaeology and the American Anthropological Association for her science writing.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus







