If German Satellite Falls on Your House, Who Pays for Repairs?
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
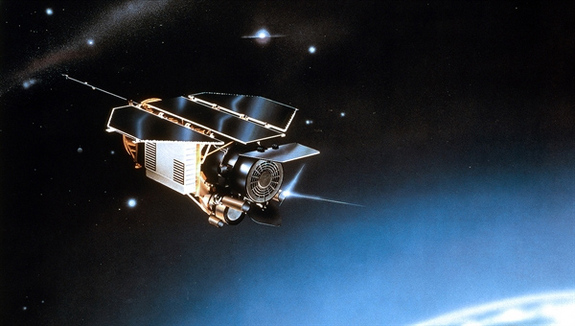
The defunct 2.7-ton German ROSAT satellite is slated to make a fiery, uncontrolled re-entry to our atmosphere sometime Saturday or Sunday (Oct. 22 or 23). Experts say the broken-up bits of ROSAT have a roughly 1-in-2,000 chance of hitting someone somewhere on Earth, though they won't know where until a few hours before it enters the atmosphere.
Let us be clear: There's an extremely remote chance that ROSAT will fall on you . But, for good measure, if ROSAT, or some other spacecraft, did fall on your property , could you keep it? And, if the bus-size satellite flattened your house, who would be on the hook for the repair bill?
First off, ROSAT was a joint venture between Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States, and remains the property of those countries even after it comes back to Earth. To keep a piece, or to try to sell it, would be illegal unless the angencies relinquish ownership of the debris. There isn't a ton of precedent here, but when people tried to sell pieces of the Space Shuttle Columbia, for example, the government shut them down, pulled their auctions from eBay and reclaimed the debris. But that was a special case because the Columbia accident was under investigation at the time. When parts of the space station Skylab landed in Australia in 1979, NASA did not reclaim them. In the present case, the trio of countries may or may not ask for ROSAT debris back. [Photos: Germany's ROSAT Satellite Falling to Earth]
The good news is that if the satellite, or even just sizable chunks of it, did in fact slam into your house, you wouldn't need to sell your new space souvenir to pay for repairs. By international law, the three countries would have to foot the bill.
Liability for damage caused by objects falling from space is regulated by the 1972 Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Objects. All three countries involved with ROSAT have signed the pact, and in doing so agreed to be "absolutely liable to pay compensation for damage caused by its space object on the surface of the Earth or to aircraft in flight." That goes if ROSAT crashes down in Kansas, France or Zimbabwe.
The terms cover just about everything. In this case, "damage" is defined as loss of life, personal injury or other impairment of health; or loss of or damage to property of states or of persons, natural or juridical, or property of international intergovernmental organizations.
And the payout is fairly good. Again, quoting the treaty: "The compensation which the launching State shall be liable to pay for damage under this Convention shall be determined in accordance with international law and the principles of justice and equity, in order to provide such reparation in respect of the damage as will restore the person, natural or juridical, State or international organization on whose behalf the claim is presented to the condition which would have existed if the damage had not occurred."
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
One slight hitch in the treaty is that you have to present your claim no later than one year following the incident (or discovery of the damage). If you've got a truck-size satellite sitting in your living room, however, we suspect that satisfying this condition would not be an issue.
- When Space Attacks: The 6 Craziest Meteor Impacts
- 6 Everyday Things that Happen Strangely in Space
- Complete Coverage of ROSAT and Other Orbital Debris
Follow Bjorn Carey on Twitter @thebjorncarey. Follow Life's Little Mysteries on Twitter @llmysteries, then join us on Facebook.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus











