How Your Nose is More Complex than a 747
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
Your nose may not be as big as a jumbo jet, or maybe it is, but whatever, it is more complex in one sense.
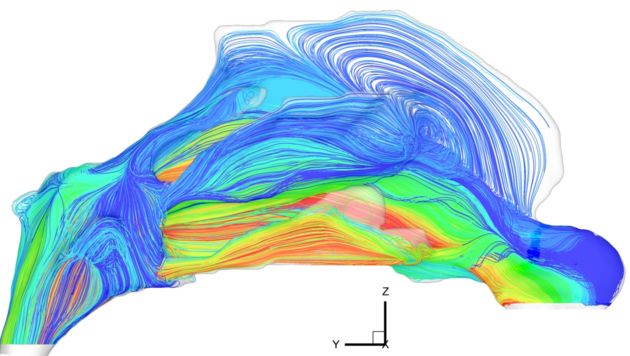
A new study of how air flows through your schnoz reveals the process to be more complicated than air coursing over a jet's wing.
Click Images to Enlarge
Images: BBSRC
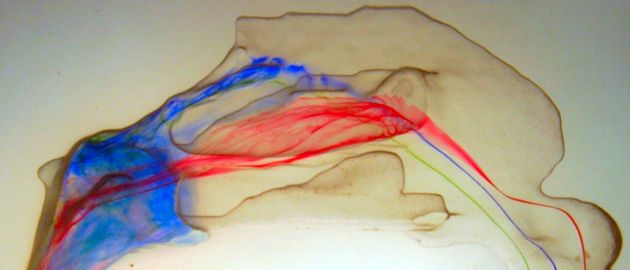
The scientists figured this out by running water laced with colored beads through a model honker. Not a model's nose, but a 3-D nose model, one twice as big as life-size. Anyway, these guys really nosed around.
"From quiet breathing to rapid sniffing, we want to know exactly what is happening," said Bob Schroter of the Imperial College London. The results clear some things up and could lead to new ways to clear up blocked nasal passages, the researchers say.
"The geometry of the nose is highly complex, with no straight lines or simple curves like an aircraft wing, and the regime of airflow is not simply laminar or turbulent," said professor Denis Doorly, assuming laminar and turbulent are simple. (Laminar means smooth, and turbulent is, well, anything but.)
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
The study revealed why we have to inhale deeply sometimes to capture a subtle scent, perhaps that of a flower.
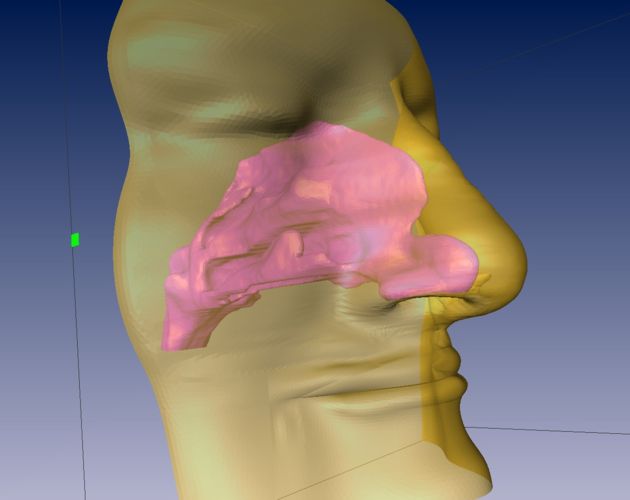
Smelling relies on getting air to the olfactory bulb, which sits somewhat inconveniently at the top of the nose, though conveniently on the inside. The way the nose is built, you have to take in a sharp breath at high velocity to shoot faint smells up there. Something like a strong gust of wind instead of a gentle breeze. Then the nose takes over, the model showed: Its structure causes air to eddy around the bulb, lingering a bit so you can enjoy the scent, or not.
The model nose was built from transparent silicone, based on CT scans "of anonymous patients found to be nasally healthy." The research beats examining cadavers, the scientist said. The findings could help surgeons plan nose jobs and allow drug companies to figure out better ways to get drugs straight into your bloodstream.
The research was announced today and is detailed in the January issue of Business, a magazine put out by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.
- The Sexy, Healthy Scent of a Man
- Engineering OJ: Terrible Smells Make Juice Fresh
- Company Making Fake Urine for Researchers
Robert is an independent health and science journalist and writer based in Phoenix, Arizona. He is a former editor-in-chief of Live Science with over 20 years of experience as a reporter and editor. He has worked on websites such as Space.com and Tom's Guide, and is a contributor on Medium, covering how we age and how to optimize the mind and body through time. He has a journalism degree from Humboldt State University in California.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus