'Sonar Anomaly' Isn't a Shipwreck, and It's Definitely Not Aliens, NOAA Says
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered Daily
Daily Newsletter
Sign up for the latest discoveries, groundbreaking research and fascinating breakthroughs that impact you and the wider world direct to your inbox.

Once a week
Life's Little Mysteries
Feed your curiosity with an exclusive mystery every week, solved with science and delivered direct to your inbox before it's seen anywhere else.

Once a week
How It Works
Sign up to our free science & technology newsletter for your weekly fix of fascinating articles, quick quizzes, amazing images, and more

Delivered daily
Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Once a month
Watch This Space
Sign up to our monthly entertainment newsletter to keep up with all our coverage of the latest sci-fi and space movies, tv shows, games and books.

Once a week
Night Sky This Week
Discover this week's must-see night sky events, moon phases, and stunning astrophotos. Sign up for our skywatching newsletter and explore the universe with us!
Join the club
Get full access to premium articles, exclusive features and a growing list of member rewards.
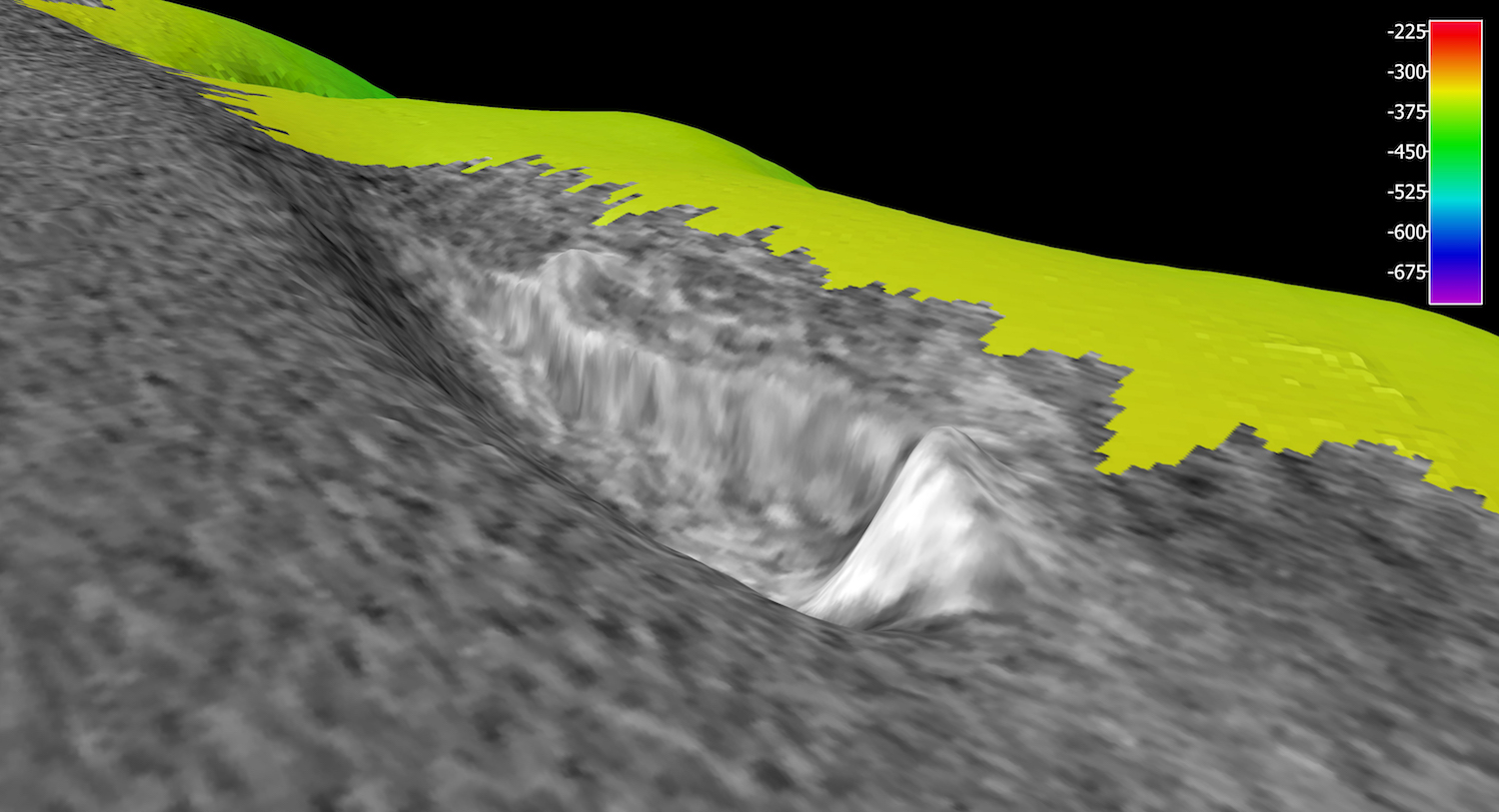
Rather, it's "geologic in origin," NOAA Ocean Explorer reported in a tweet yesterday (June 27).
The finding, although not surprising, is a bit of a letdown after NOAA tweeted earlier that day that the anomaly could be "an archaeology site, a geological formation or otherwise!" [Photos: Colonial-Age Shipwrecks Found Off Cape Canaveral Coast]
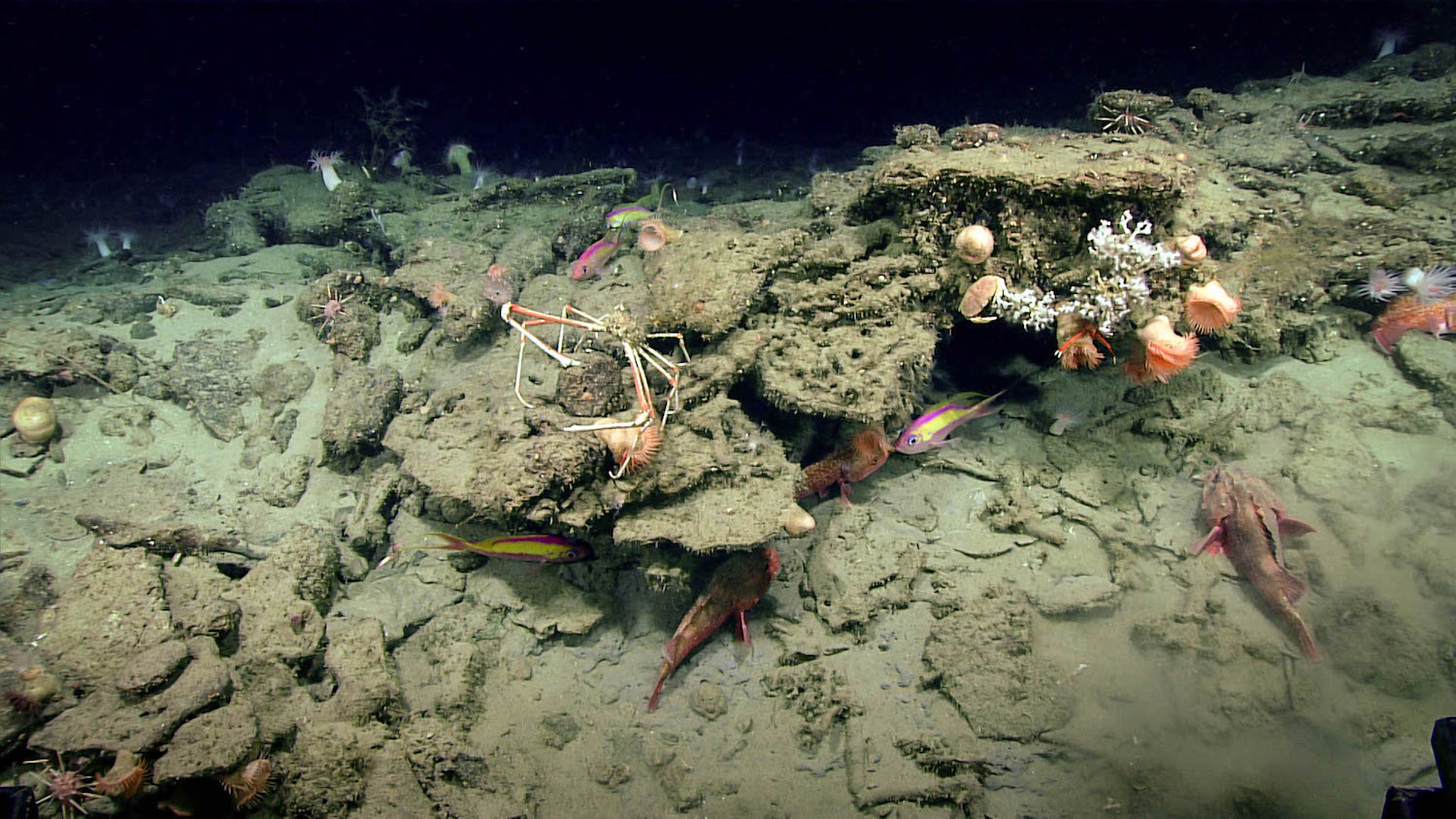
Scientists aboard NOAA's Okeanos Explorer noticed the anomaly while mapping the seafloor off the coast of North Carolina. They dubbed the site the "Big Dipper" anomaly and promptly sent a remotely operated vehicle (ROV) underwater to investigate.
Given that North Carolina's coast is called the "Graveyard of the Atlantic," because of the many shipwrecks discovered in the area, NOAA scientists initially speculated that the anomaly could be the remains of a long-lost ship, according to The Charlotte Observer.
But the ROV found otherwise. The anomaly turned out to be a "rocky feature," NOAA said in a tweet. On the upside, this feature "is great habitat for many species, including the many fish already seen," NOAA noted.
The Okeanos Explorer's current expedition — called Windows to the Deep 2018: Exploration of the Southeast U.S. Continental Margin— is helping NOAA researchers map the seafloor in unknown and poorly understood deepwater areas of the southeastern United States, according to the expedition's mission plan. The expedition began on May 22 and runs through July 2.
Parts of the expedition included mapping "unexplored areas of the Blake Plateau, Blake Ridge, Blake Escarpment, submarine canyons offshore of North Carolina, submerged cultural heritage sites, areas predicted to be suitable habitat for deep-sea corals and sponges, inter-canyon areas, and gas seeps," NOAA said.
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Meanwhile, the ROV dives are helping scientists understand the "diversity and distribution of deepwater habitats in this region," NOAA said.
However, aliens and unknown shipwrecks don't seem to be a part of that underwater world, at least not yet.
Original article on Live Science.

Laura is the managing editor at Live Science. She also runs the archaeology section and the Life's Little Mysteries series. Her work has appeared in The New York Times, Scholastic, Popular Science and Spectrum, a site on autism research. She has won multiple awards from the Society of Professional Journalists and the Washington Newspaper Publishers Association for her reporting at a weekly newspaper near Seattle. Laura holds a bachelor's degree in English literature and psychology from Washington University in St. Louis and a master's degree in science writing from NYU.
 Live Science Plus
Live Science Plus