Cold Case Closed: 'Iceman' Mummy Bled to Death
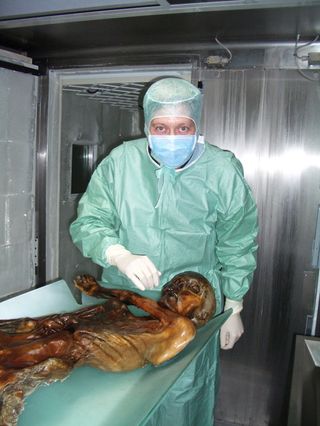
Archaeologists have determined the cause of death of the “Iceman” mummy, putting to rest a Neolithic cold case. More than 5,000 years ago, a man trekked up the Schnalstal glacier in Italy and died. The mummified, frozen body, dubbed Ötzi, was discovered in 1991 by accident. Since then, the glacier mummy has undergone a slew of examinations from which scientists have gleaned bits of information about the man’s last steps on Earth, ranging from his last meal to his age when he died (45). The remaining question: What caused the Iceman’s sudden death? Frank Rühli of the Institute of Anatomy at the University of Zurich in Switzerland and his colleagues scanned the mummy’s body using computed tomography (CT) and found a lesion of an artery near the shoulder, underneath the clavicle bone. The wound was caused by an arrowhead, which had previously been detected, lodged into the mummy’s back. In tissues surrounding the lesion, the scientists found a large hematoma, or bruise. By combining historic and modern data on how well one survives such a severe lesion, the scientists concluded that the Iceman died within a short time as a result of this lesion. The arrowhead-caused injury caused the Iceman to drop dead. "It basically means [the Iceman] would bleed to death," Rühli told LiveScience. “Such obvious proof of a vascular lesion in a body of this historic age is unique, and it helped to determine the cause of this extraordinary death without a destructive autopsy,” Rühli said. “We look forward to further investigating the circumstances surrounding the Iceman’s sudden death.”
In addition, Rühli said the case is more than just a medical and archaeological curiosity. "We want to have more knowledge of life and death in ancient times to learn more about the evolution of diseases," he explained, referring to the study of ancient diseases as the fourth dimension of medicine. The research is published online in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
- CSI: Egypt
- King Tut Not Murdered, CT Scan Shows
- Urban Legends Debunked
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Jeanna served as editor-in-chief of Live Science. Previously, she was an assistant editor at Scholastic's Science World magazine. Jeanna has an English degree from Salisbury University, a master's degree in biogeochemistry and environmental sciences from the University of Maryland, and a graduate science journalism degree from New York University. She has worked as a biologist in Florida, where she monitored wetlands and did field surveys for endangered species. She also received an ocean sciences journalism fellowship from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution.
Most Popular


