7 bizarre ancient cultures that history forgot
Long-Lost Cultures

The ancient Egyptians had their pyramids, the Greeks, their sculptures and temples. And everybody knows about the Maya and their famous calendar.
But other ancient peoples get short shrift in world history. Here are a handful of long-lost cultures that don't get the name recognition they deserve.
The Silla
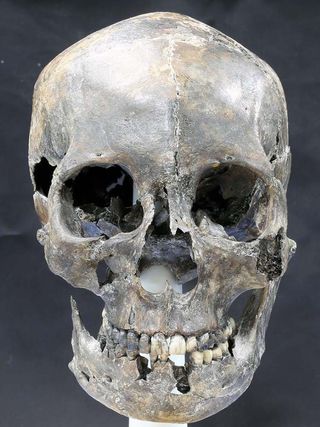
The Silla Kingdom was one of the longest-standing royal dynasties ever. It ruled most of the Korean Peninsula between 57 B.C. and A.D. 935, but left few burials behind for archaeologists to study.
One recent Silla discovery gave researchers a little insight, however. The intact bones of a woman who lived to be in her late 30s was found in 2013 near the historic capital of the Silla (Gyeongju). An analysis of the woman's bones revealed that she was likely a vegetarian who ate a diet heavy in rice, potatoes or wheat. She also had an elongated skull.
Silla was founded by the monarch Bak Hyeokgeose. Legend held that he was hatched from a mysterious egg in the forest and married a queen born from the ribs of a dragon. Over time, the Silla culture developed into a centralized, hierarchical society with a wealthy aristocratic class. Though human remains from the Silla people are rare, archaeologists have unearthed a variety of luxurious goods made by this culture, from a gold-and-garnet dagger to a cast-iron Buddha to jade jewelry, among other examples held at the Gyeongju National Museum in South Korea. [See Images of the Long-Headed Woman's Facial Reconstruction]
The Indus

The Indus is the largest-known ancient urban culture, with the people's land stretching from the Indus River in modern-day Pakistan to the Arabian Sea and the Ganges in India. The Indus civilization persisted for thousands of years, emerging around 3300 B.C. and declining by about 1600 B.C.
The Indus, also known as the Harappans, developed sewage and drainage systems for their cities, built impressive walls and granaries, and produced artifacts like pottery and glazed beads. They even had dental care: Scientists found 11 drilled molars from adults who lived between 7,500 to 9,000 years ago in the Indus Valley, according to a study published in 2006 in the journal Nature. A 2012 study suggested that climatic change weakened monsoonal rains and dried up much of the Harappan territory, forcing the civilization to gradually disband and migrate to wetter climes.
The Sanxingdui

The Sanxingdui were a Bronze Age culture that thrived in what is now China's Sichuan Province. A farmer first discovered artifacts from the Sanxingdui in 1929; excavations in the area in 1986 revealed complex jade carvings and bronze sculptures 8 feet (2.4 meters) tall.
But who were the Sanxingdui? Despite the evidence of the culture's artistic abilities, no one really knows. They were prolific makers of painted bronze-and-gold-foil masks that some archaeologists believe may have represented gods or ancestors, according to the Sanxingdui Museum in China. The Sanxingdui site shows evidence of abandonment about 2,800 or 3,000 years ago, and another ancient city, Jinsha, discovered nearby, shows evidence that maybe the Sanxingdui moved there. In 2014, researchers at the annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union argued that at around this time, a major earthquake and landslide redirected the Minjiang River, which would have cut Sanxingdui off from water and forced a relocation.
The Nok

The mysterious and little-known Nok culture lasted from around 1000 B.C. to A.D. 300 in what is today northern Nigeria. Evidence of the Nok was discovered by chance during a tin-mining operation in 1943, according to the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York. Miners uncovered a terra-cotta head, hinting at a rich sculptural tradition. Since then, other elaborate terra-cotta sculptures have emerged, including depictions of people wearing elaborate jewelry and carrying batons and flails — symbols of authority also seen in ancient Egyptian art, according to the Minneapolis Institute of Art. Other sculptures show people with diseases such as elephantiasis, the Met said.
Contributing to the mystery surrounding the Nok, the artifacts have often been removed from their context without archaeological analysis. In 2012, the United States returned a cache of Nok figurines to Nigeria after they were stolen from Nigeria's national museum and smuggled into the U.S.
The Etruscans

The Etruscans had a thriving society in northern Italy from about 700 B.C. to about 500 B.C., when they began to be absorbed by the Roman Republic. They developed a unique written language and left behind luxurious family tombs, including one belonging to a prince that was first excavated in 2013.
Etruscan society was a theocracy, and their artifacts suggest that religious ritual was a part of daily life. The oldest depiction of childbirth in Western art — a goddess squatting to give birth — was found at the Etruscan sanctuary of Poggio Colla. At the same site, archaeologists found a 4-foot by 2-foot (1.2 by 0.6 meters) sandstone slab containing rare engravings in the Etruscanlanguage. Few examples of written Etruscan survive. Another Etruscan site, Poggio Civitate, was a square complex surrounding a courtyard. It was the largest building in the Mediterranean at its time, said archaeologists who have excavated more than 25,000 artifacts from the site.
The Land of Punt

Some cultures are known mostly through the records of other cultures. That's the case with the mysterious land of Punt, a kingdom somewhere in Africa that traded with the ancient Egyptians. The two kingdoms were exchanging goods from at least the 26th century B.C., during the reign of the pharaoh Khufu (the builder of the Great Pyramid of Giza).
Strangely, no one really knows where Punt was located. The Egyptians left plenty of descriptions of the goods they got from Punt (gold, ebony, myrrh) and the seafaring expeditions they sent to the lost kingdom. However, the Egyptians are frustratingly mum on where all these voyages were headed. Scholars have suggested that Punt may have been in Arabia, or on the Horn of Africa, or maybe down the Nile River at the border of modern-day South Sudan and Ethiopia.
The Bell-Beaker Culture

You know a culture is obscure when archaeologists name it based on its artifacts alone. The Bell-Beaker culture made pottery vessels shaped like upside-down bells. The makers of these distinctive drinking cups lived across Europe between about 2800 B.C. and 1800 B.C. They also left behind copper artifacts and graves, including a cemetery of 154 graves located in the modern-day Czech Republic.
The Bell-Beakers were also responsible for some of the construction at Stonehenge, researchers have found: These people likely arranged the site's small bluestones, which originated in Wales.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Stephanie Pappas is a contributing writer for Live Science, covering topics ranging from geoscience to archaeology to the human brain and behavior. She was previously a senior writer for Live Science but is now a freelancer based in Denver, Colorado, and regularly contributes to Scientific American and The Monitor, the monthly magazine of the American Psychological Association. Stephanie received a bachelor's degree in psychology from the University of South Carolina and a graduate certificate in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
